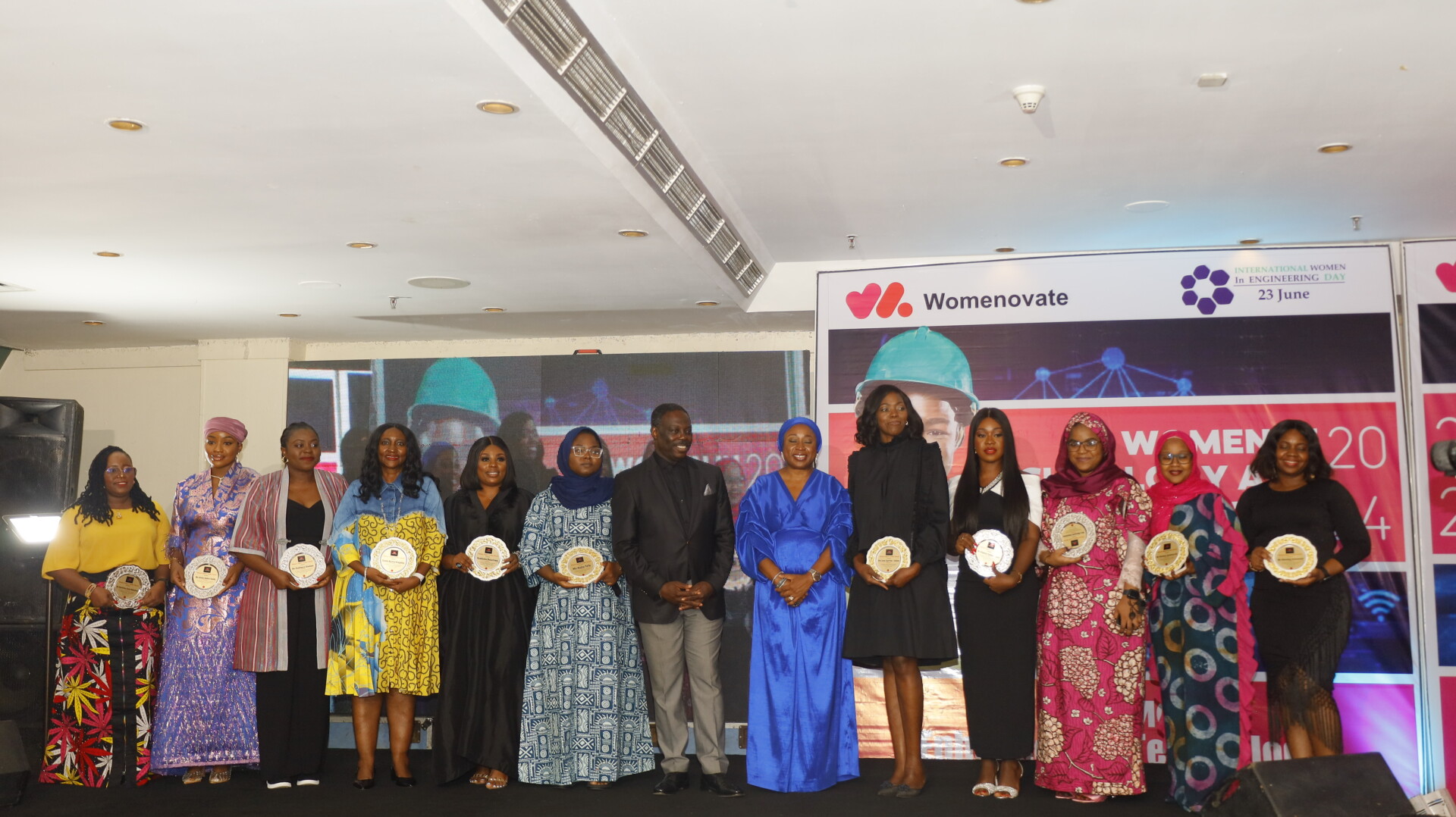
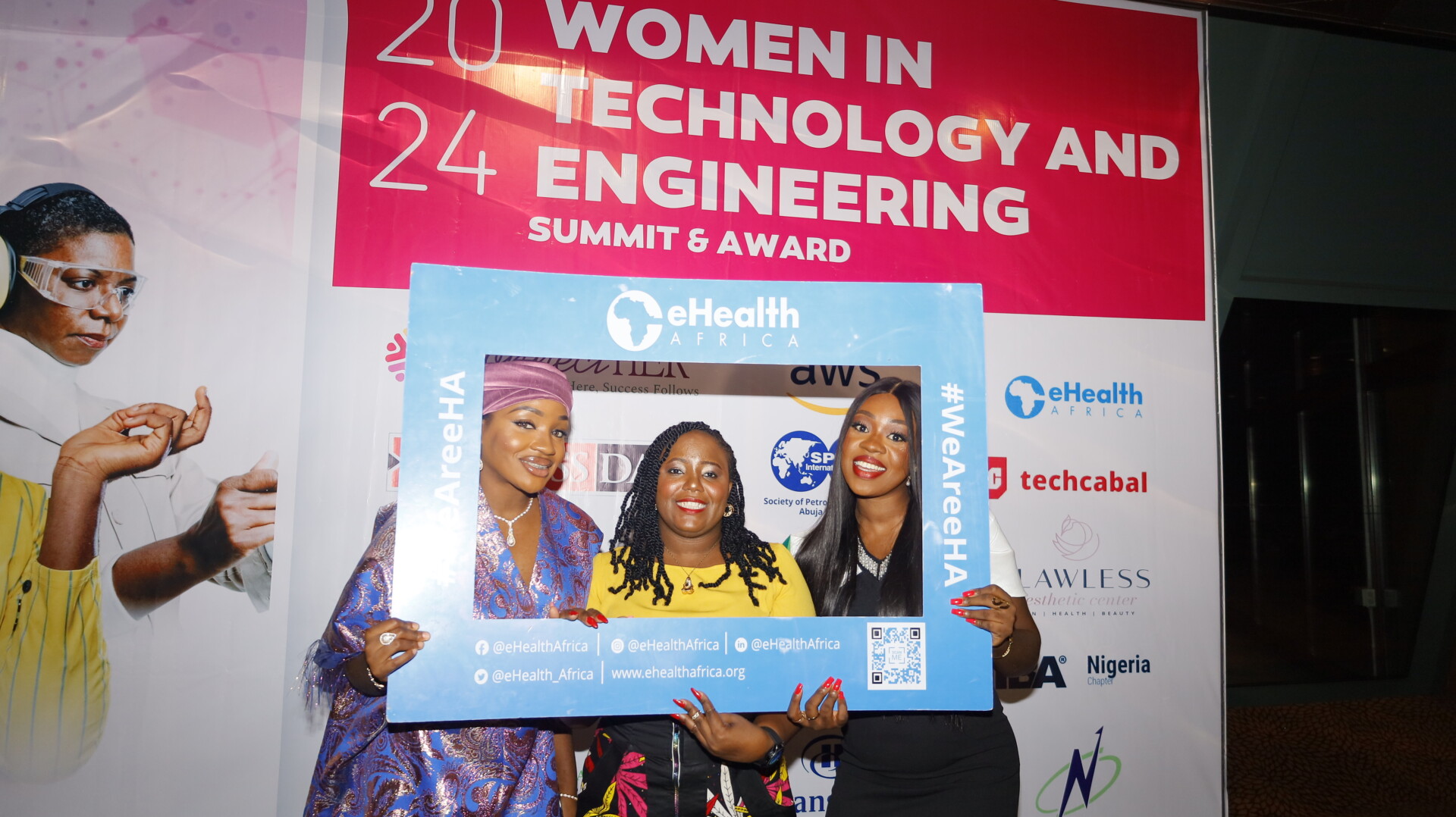
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, women are making significant strides, overcoming barriers, and reshaping industries that have traditionally been male-dominated. One such trailblazer is Ms. Diligence Saviour, Business Application Senior Coordinator at eHealth Africa, who has recently been recognized as one of the 2024 Women in Technology and Engineering Award recipients. Presented by Womenovate, this prestigious award highlights her invaluable contributions to public health initiatives through her expertise in technology.
We had the privilege to sit down with Ms. Saviour and delve into her inspiring journey, one that highlights not only her passion for technology but also her determination to succeed in an environment often filled with challenges. In this candid interview, she shares her background, early influences, and the profound lessons learned throughout her career. Ms. Saviour’s story is a testament to perseverance, hard work, and the belief that gender should never be a barrier to achieving one’s dreams.
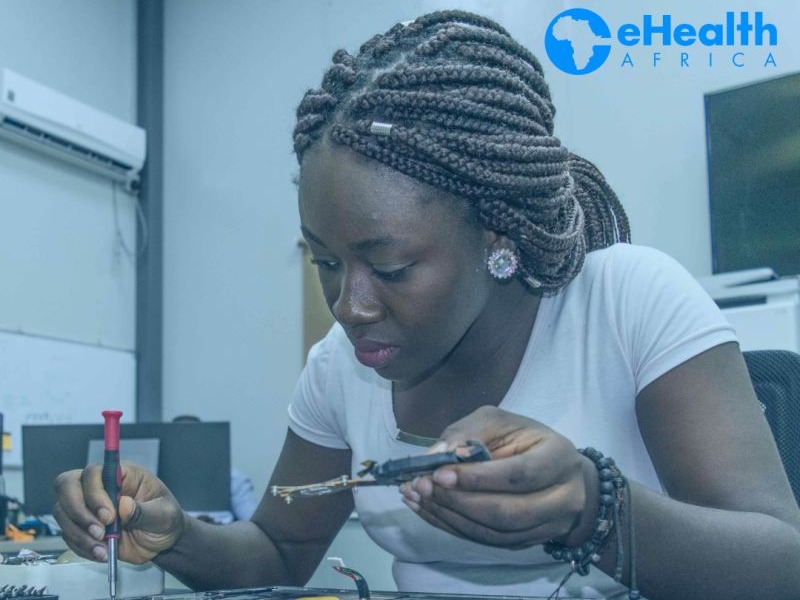

QUESTION 1: Tell us something about yourself and your background.
ANSWER:
My name is Diligence Saviour. I am from Bayelsa state. I have four siblings – two girls and three boys. My mom passed away some time ago, and my father works as a registrar at a university. I obtained my first degree in computer science from Niger Delta University in 2014. In 2021, I enrolled in a master’s degree program in computer applications at Bayero University Kano. Along the way, I also earned several certifications, including project management, Scrum Master, and IT.
QUESTION 2: What was your dream job as a child?
ANSWER:
As a child, I loved art, but my father wanted me to become a medical doctor. Following his wishes, I pursued the sciences. During my JAMB exams, I chose Medicine and Pharmacy as my study options. I was admitted to study pharmacy even before my WAEC results were out. However, when the results were finally released, I couldn’t continue with pharmacy due to incomplete results. Left with limited choices, I had to pick between Mathematics and Computer Science. I chose computer science with the idea of retaking JAMB to study Medicine and Surgery. But during my first year in computer science, I developed a deep passion for the field, and I decided to continue with it. And as they say, the rest is history.
QUESTION 3: What attracted you to your current role?
ANSWER:
I’ve always had a knack for getting things done. As an undergraduate, I noticed that my classmates often struggled with software applications on their phones, and I would eagerly troubleshoot and fix their issues. The satisfaction of solving problems for others gave me so much joy. That same drive led me to a career in IT support, where I learned to troubleshoot networks and various system issues, and that’s how I found my path in this field.
QUESTION 4: How were your first days in this career?
ANSWER:
They were tough. Each day presented new challenges, new issues to resolve, and new things to learn. I began as an IT support personnel, which involved a lot of physical work, like rolling cables, clipping cables, and even climbing ladders. Back then, it wasn’t considered the “coolest” job for a lady due to the stereotypes associated with women in such roles, but I pushed through and grew in the profession.
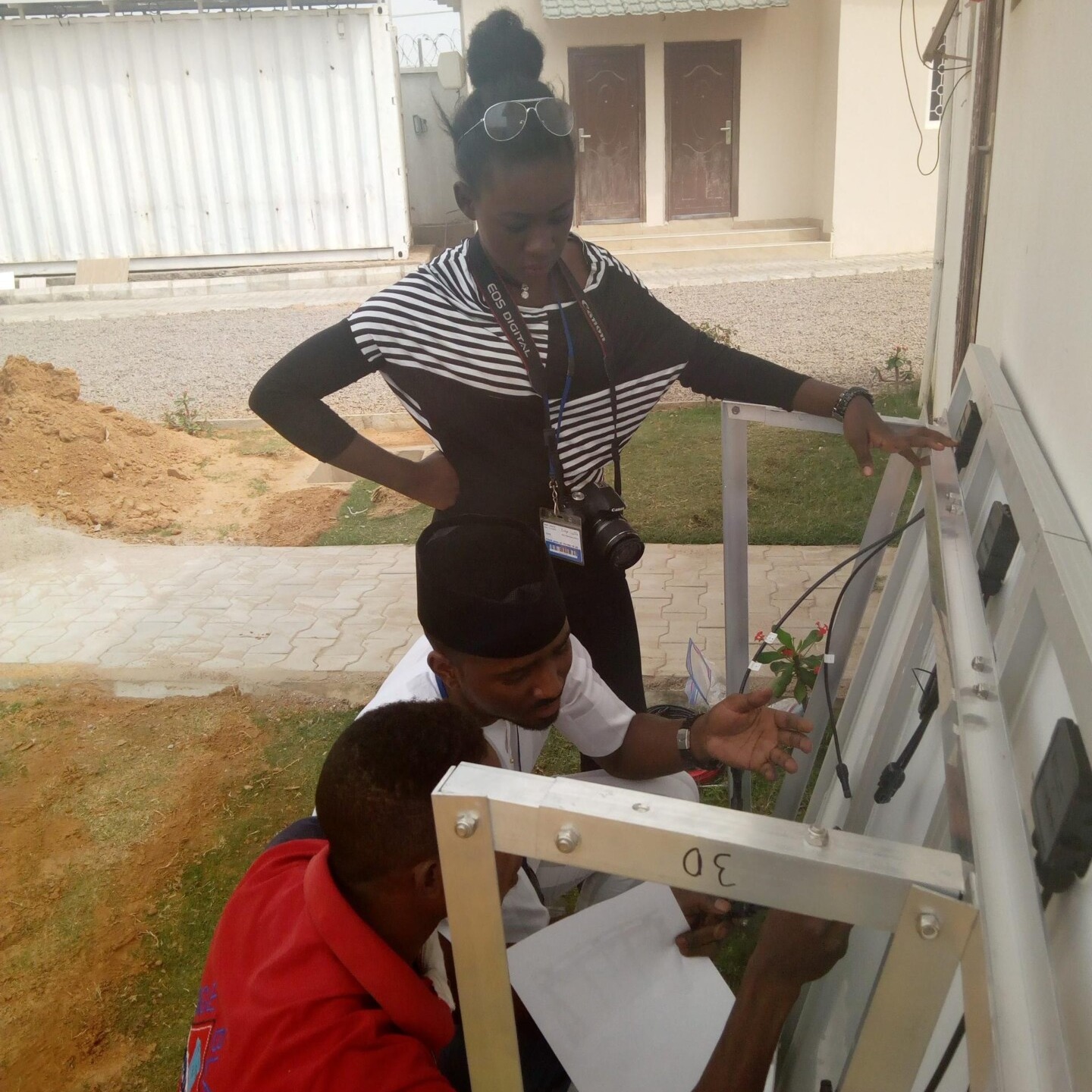

QUESTION 5: How does it feel to be recognized with this award for your contributions to global health initiatives?
ANSWER:
It’s an amazing feeling! Just being nominated was a great source of motivation, but actually winning the award pushes me to strive for even greater excellence. It’s a reminder that my contributions are making a difference and inspires me to continue pushing for change in my space.
QUESTION 6: What are some of your proudest accomplishments while working on global health initiatives at eHealth Africa?
ANSWER:
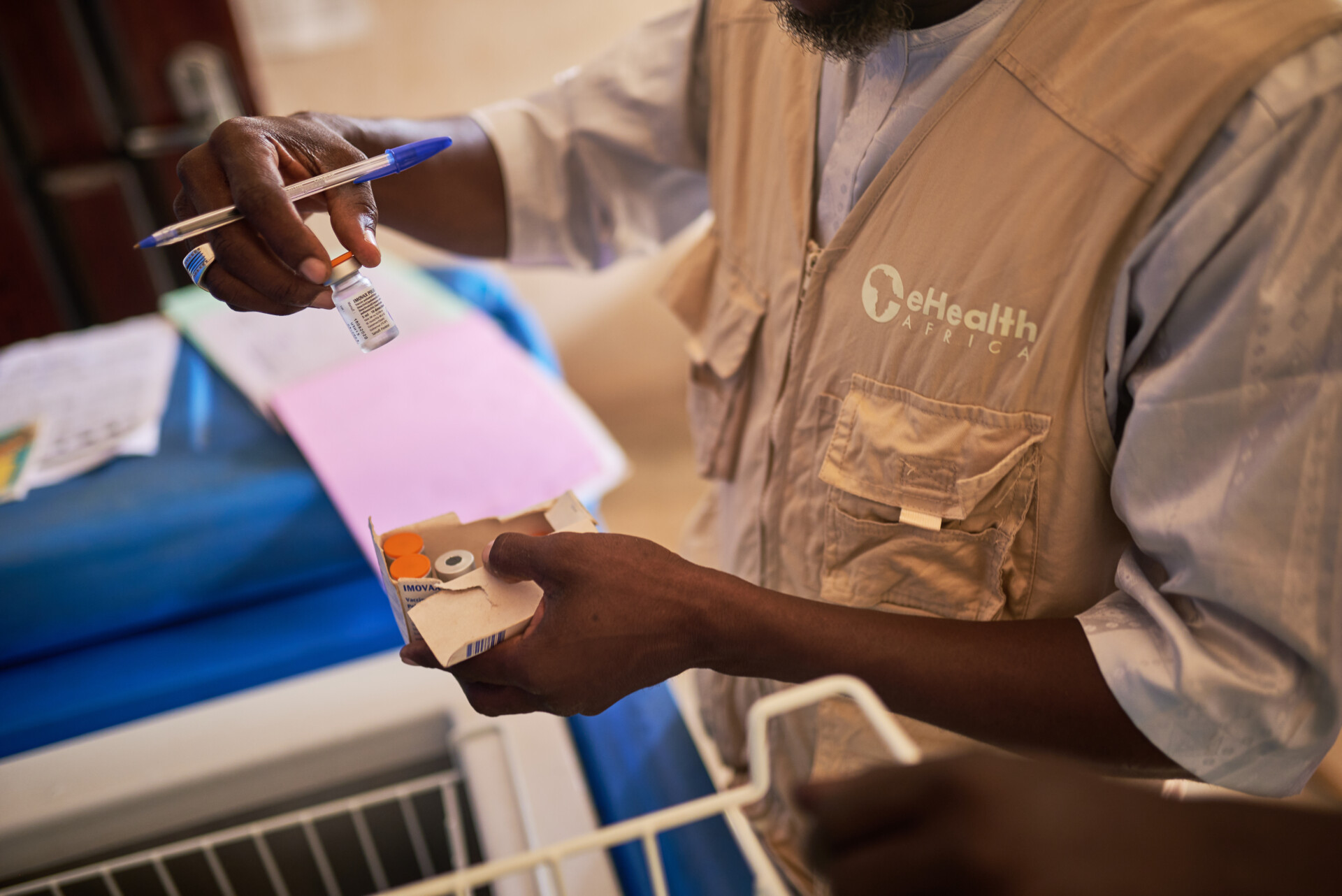
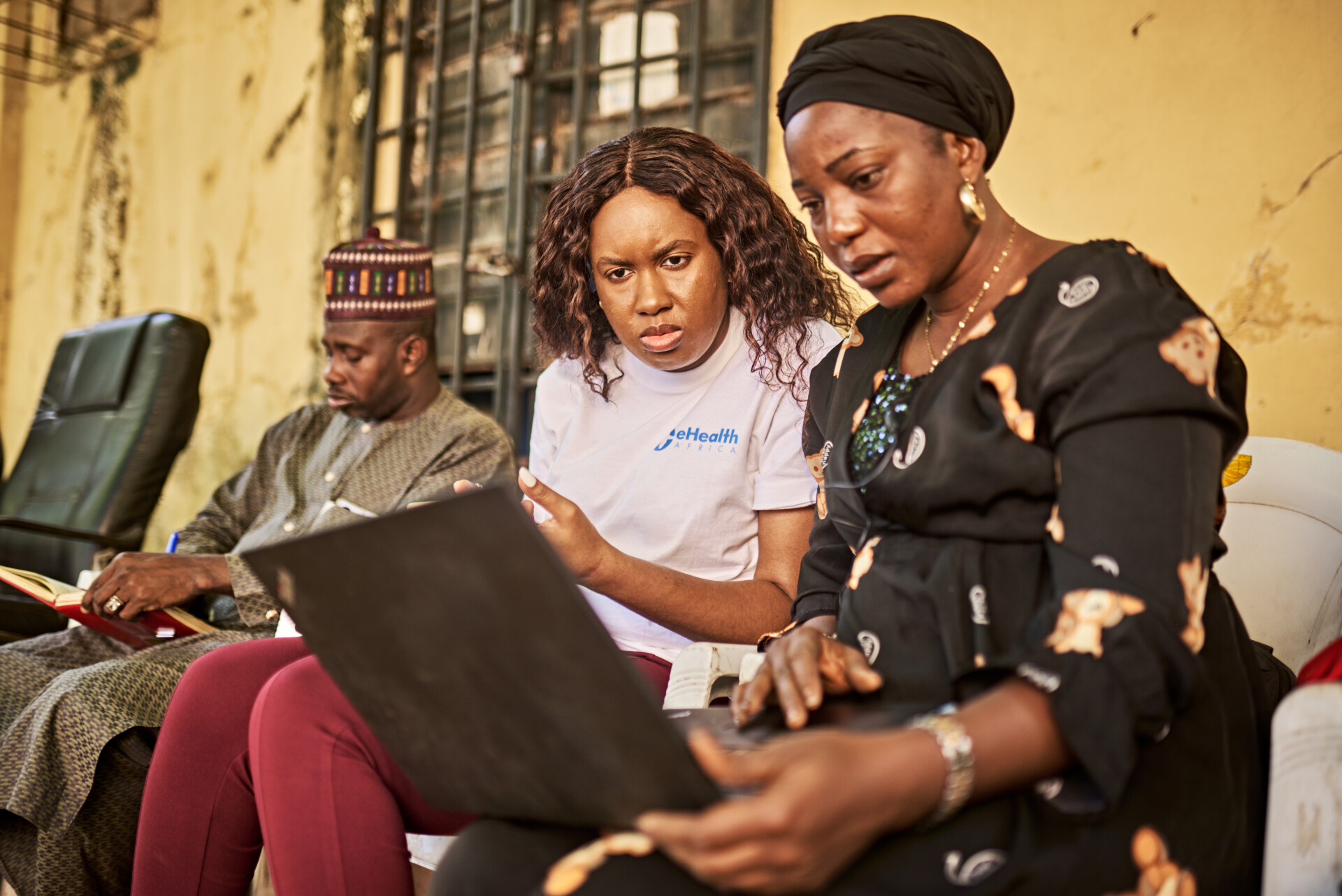
I started as IT support and have since grown into the role of Business Application Senior Coordinator. I manage critical software applications for eHealth Africa, like INFOSEC and Sage X3, which are used across all our offices globally, including in the USA, Germany, Sierra Leone, and Nigeria. I’m proud to say that I’ve trained over 300 staff members, covering everything from procurement to project management processes. Providing technical support to our teams and ensuring they can effectively use these applications has been a huge part of my journey, and it’s incredibly rewarding.
QUESTION 7: Who has been your biggest mentor or influence in your career?
ANSWER:
One of my most significant influences was Esosa Olia. When I first started my career in IT support, I worked closely with her. She was responsible for managing our enterprise resource application, and I admired how she seamlessly handled tasks and solved problems. Her work ethic and dedication taught me that with enough determination and hard work, I could achieve anything. Esosa has had a lasting impact on my career.
QUESTION 8: You work in a male-dominated discipline. What challenges have you faced as a woman in that environment, and how did you deal with them?
ANSWER:
I’ve had many challenging experiences. For example, I once had to fix a surveillance camera in Nigeria, and while I was on a ladder, a man started shouting at me in Hausa, angry that a woman was on a ladder doing such work. That experience unsettled me, but it was a reminder of the stereotypes women face in this field. Despite such situations, I remained focused and determined to prove myself in the industry.
QUESTION 9: What is the best professional advice you’ve ever received?
ANSWER:
The best advice I’ve received is related to procrastination. I once heard someone say, “For everything that you start, you can only finish if you don’t procrastinate.” The more you procrastinate, the more your workload grows. That advice stuck with me, and I try my best to avoid procrastination whenever possible.
QUESTION 10: What advice would you give to young women aspiring to enter the field of global health?
ANSWER:
The tech field is constantly evolving, so you need to continuously learn and upgrade your skills to grow. Many women may choose easier career paths, but for those aspiring to enter tech, it’s essential to know what you want and pursue that knowledge with passion. You can achieve anything you set your mind to!
As we conclude this insightful conversation with Ms. Diligence Saviour, we celebrate not just her achievements but also the role that eHealth Africa plays in supporting women in tech. Through our dedication to fostering inclusive work environments, eHealth Africa ensures that talented professionals like Ms. Saviour have the opportunity to excel and make lasting contributions to global health initiatives. Ms. Saviour’s story is a powerful reminder that gender should never be a barrier to success in any industry, especially one as impactful as technology in global health.
Contact:
Tijesu Ojumu
Communications Coordinator eHealth Africa