Moshood Isah
More than half of the world’s population growth between now and 2050 will take place in Africa, where 1.3-billion people are expected to be born by mid-century. This potential growth unfortunately doesn’t seem to match digital technological skills needed to ensure this growing population fulfills its potential.
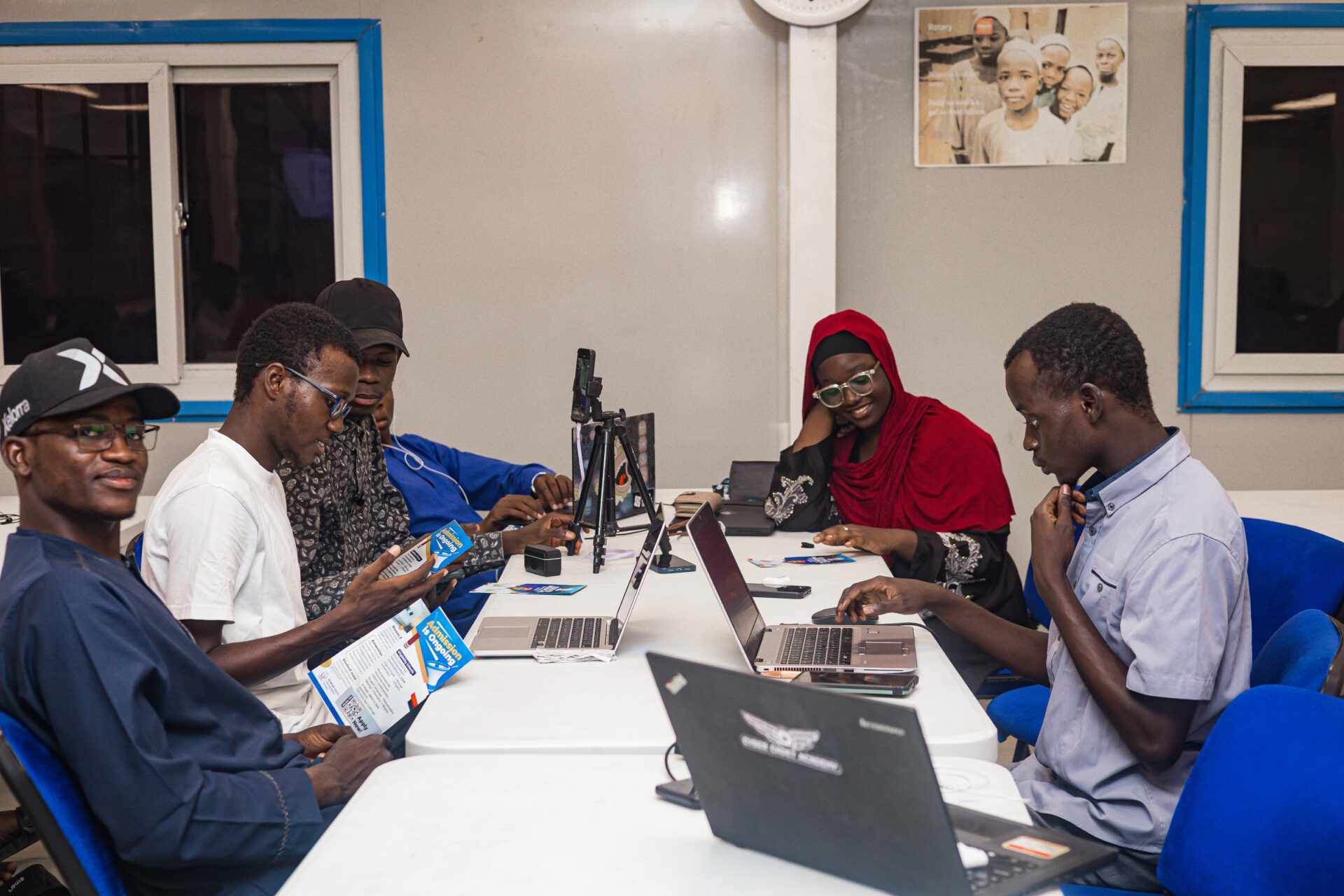
The ‘Africa’s Tech Skills Scarcity Revealed‘ report found that a lack of skills is having a negative effect on the continent’s digital transformation efforts. Organizations from Africa in this vein have continued to make concerted effort to bridge these gaps. In northern Nigeria, eHealth Africa and Desert Sky Exploration are taking bold steps to provide platforms for young people through the NASA apps challenge.
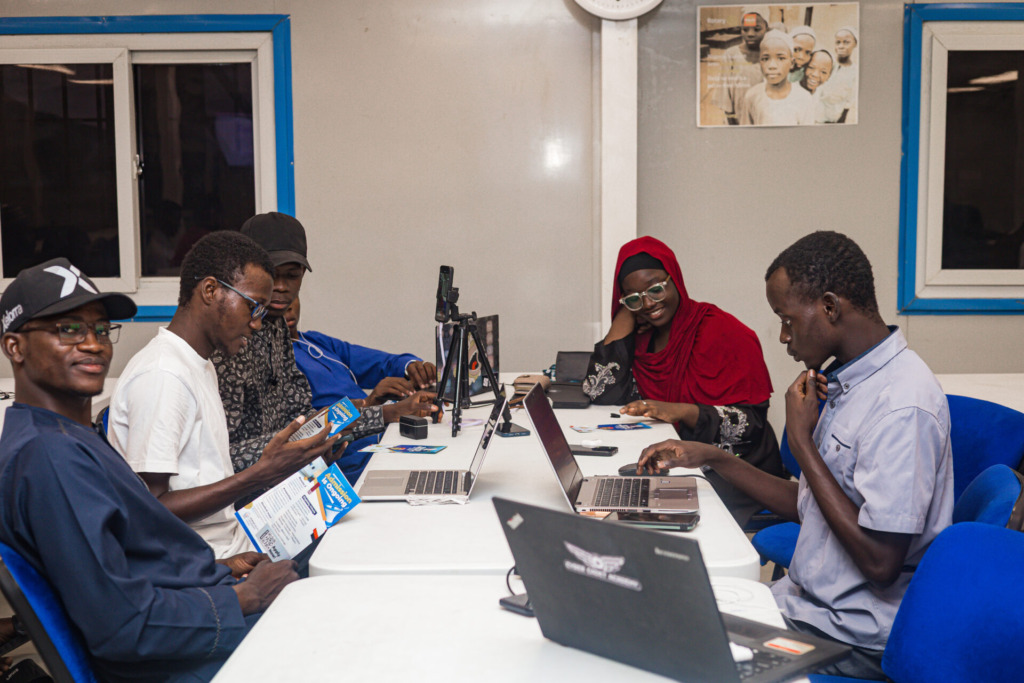

As part of its commitment to driving digital innovation across Africa, eHealth Africa (eHA) continues to champion this initiative as a strategic platform for empowering local talent and strengthening the innovation ecosystem in Kano State and across Nigeria. For the third consecutive year, eHA has proudly supported the NASA Space Apps Challenge; Kano State Chapter, not only by providing a digitally equipped facility but also by engaging digital experts to serve as chief judges for the challenge.
The global innovation event is regarded as the world’s largest annual hackathon, bringing together problem-solvers, developers, designers, and storytellers to create open-source solutions that address some of Earth’s most pressing challenges.
Speaking on the partnership between eHealth Africa and Desert Sky Exploration for the NASA Space Apps Challenge, the Deputy Director of Global Health Informatics, Abdulhamid Yahaya, said that supporting the challenge is a strategic investment in the future of local innovation. He noted that the event provides a global platform for young developers, data scientists, and creatives in Kano to work with real NASA data, apply digital tools, and co-create solutions with global relevance.

He explained, “By supporting this initiative, eHA helps to foster a culture of innovation that encourages data-driven thinking and collaborative problem-solving — building digital skills among youth and equipping them for future opportunities in technology, health, and development.”
According to him, “This intervention bridges global and local knowledge ecosystems, bringing world-class opportunities to communities that are often left out of global conversations.”
He added, “Similarly, by connecting participants with mentors, government stakeholders, academia, and the private sector, eHealth Africa helps create an ecosystem that sustains innovation beyond a single event.”
In a similar vein, the Local Lead for Kano State, Abdul Gumel, said the NASA Space Apps Challenge is “beyond just a competition; it is a catalyst that gives young people the opportunity to collaborate and develop innovative solutions that can be transformed into real-time, problem-solving products.”
According to him, “eHealth Africa’s partnership remains instrumental, especially in areas such as climate change, health, and other technologically driven sectors.”
Participants are mainly young, enthusiastic individuals, students and budding innovators who are ready to take bold steps toward change. One such participant is Aliyu Usman Bello, a Pharmacy student at Bayero University, Kano. Concerned about the devastation caused by floods in communities such as Mubi, Adamawa State, Aliyu and his team decided to work on a weather prediction system that could forecast conditions in advance.
He said, “We’re trying to build something that will last for five, ten, even twenty years — something that helps us understand how the climate and environmental landscape will evolve in the coming years and enables people to prepare for those changes in advance.”
Aliyu is excited about the networking opportunities and the chance to collaborate on innovative ideas with his team members and colleagues from other groups.
On her part, Odika Ayomide, a chemical engineer, expressed her excitement at being able to use NASA’s Space Apps open data to solve real-world problems.
She explained, “Our project focuses on identifying waste accumulation hotspots, improving coordination between communities and waste management agencies, and implementing efficient waste pickup systems.”
According to her, the goal is to make waste management smarter and more sustainable — helping cities stay cleaner while promoting community engagement and data-driven decision-making.
Looking ahead, Abdulhamid Yahaya noted that there will be post-event incubation and mentorship opportunities to support winning and promising teams through technical guidance, access to data, and coaching to refine and deploy their solutions. He added, “There is also the potential to connect innovators with funding opportunities and collaborators who can help scale their ideas into operational projects.”
The NASA Space Apps Challenge represents more than just an event — it is a movement of thinkers, builders, and changemakers united by curiosity and creativity. For eHealth Africa, being part of this journey reflects its broader commitment to empowering communities through data, innovation, and technology. As eHA continues to champion this initiative, the organization reaffirms its belief that when innovation is inclusive, local, and purpose-driven, the possibilities are limitless.