By Moshood Isah
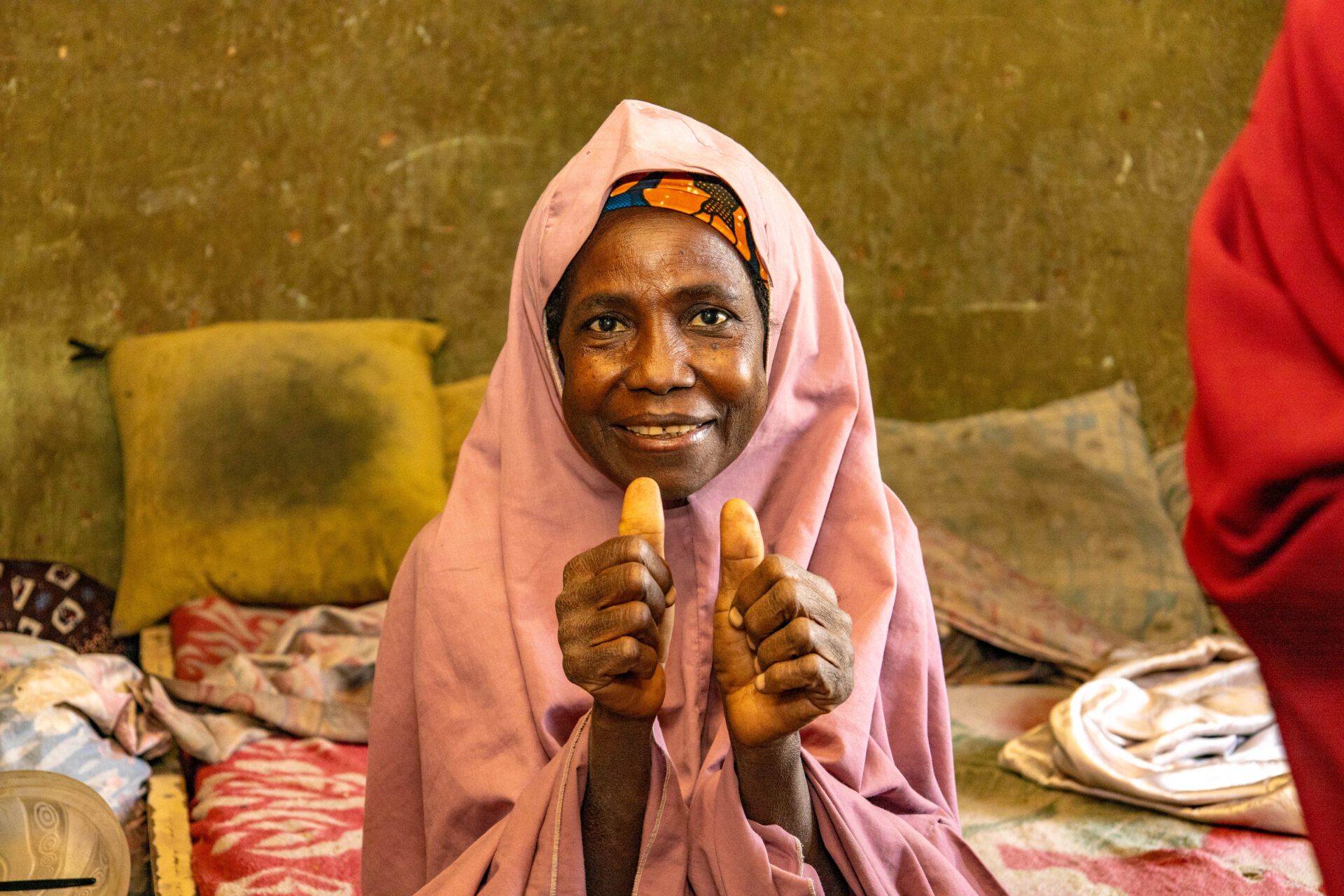
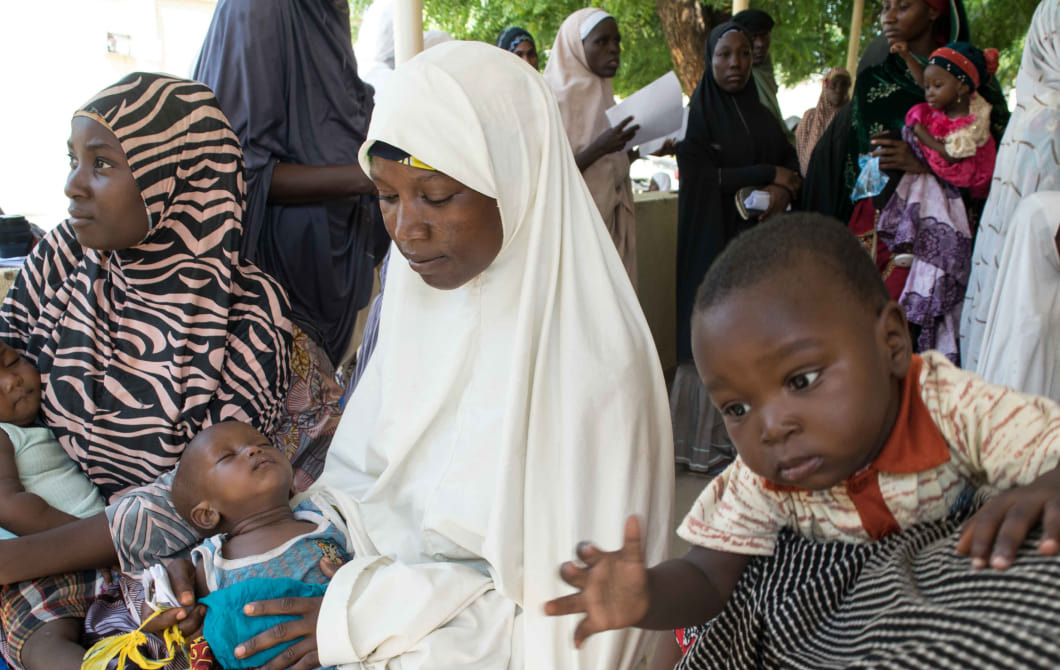
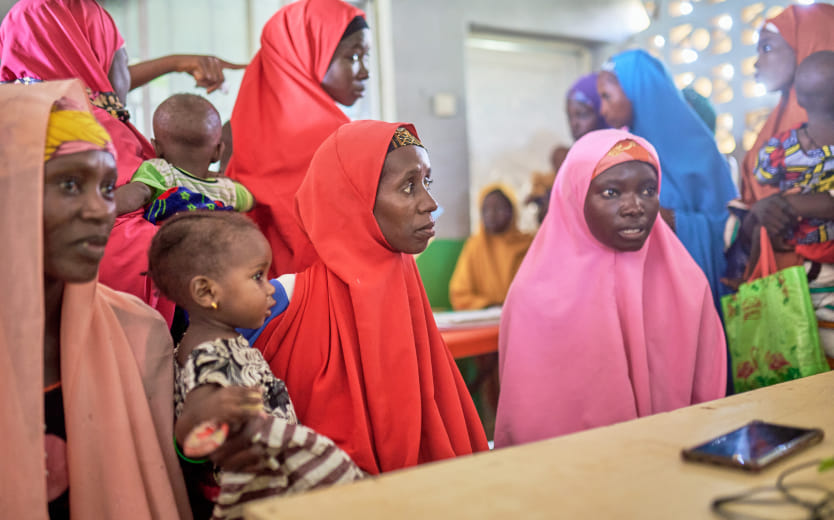
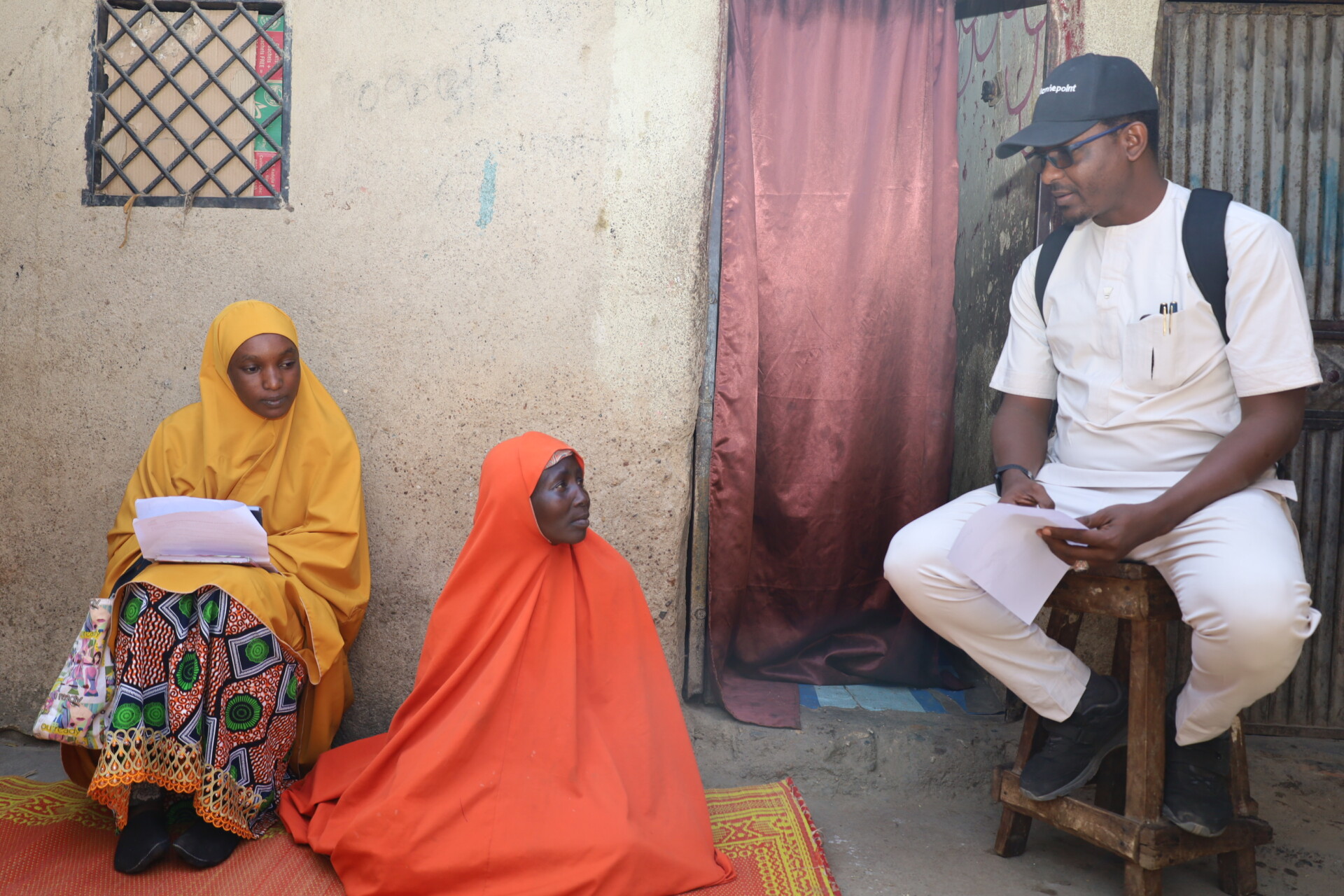
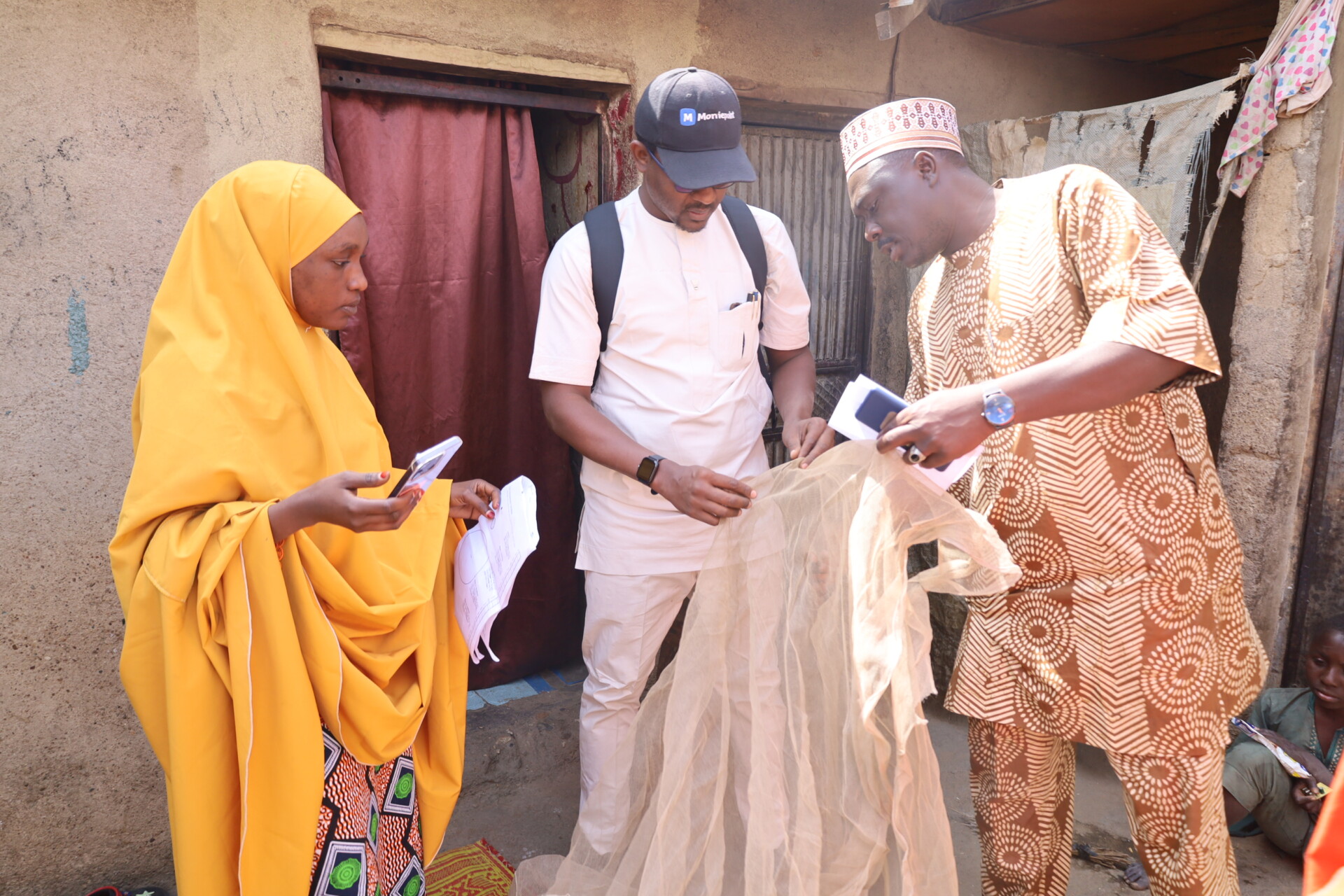
In Kano, Nigeria—where healthcare resources are often limited—Hafsat’s story stands as a powerful testament to hope and transformation, made possible through the free medication initiative under eHealth Africa’s ‘Digitizing for Impact: Improving Rural Access to Integrated Services for NCDs in Nigeria (DIIAN)’ intervention.
Struggling with hypertension and an ulcer for years, Hafsat’s health journey was full of frustration and uncertainty. Yet, after discovering the EHA REACH Clinic, a key partner in the DIIAN intervention offering free, targeted care, her life took a turn for the better.
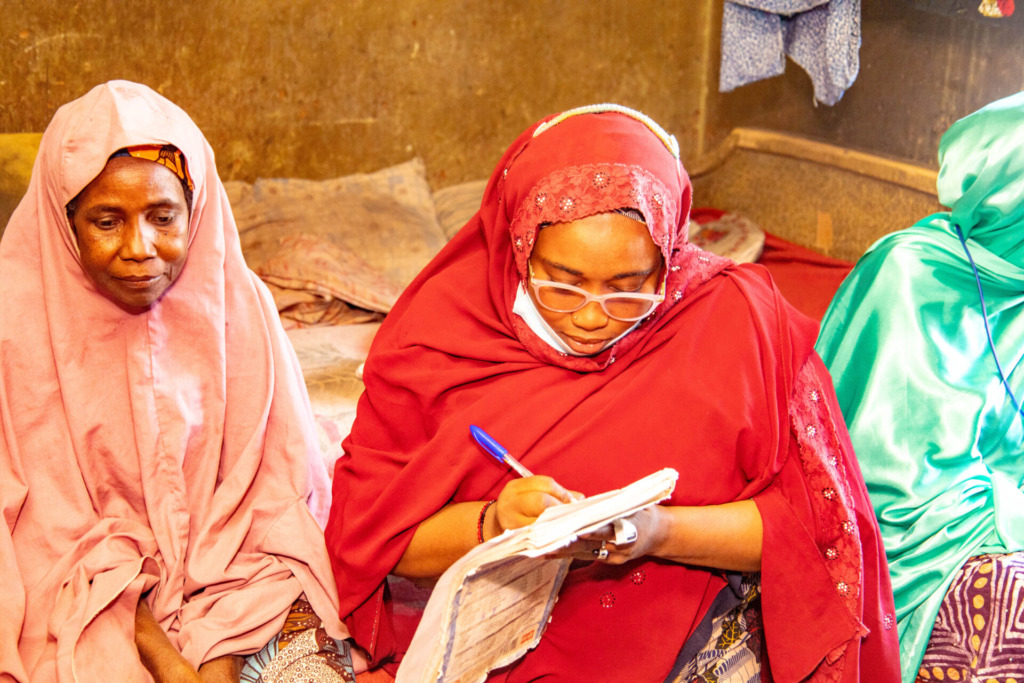

Hafsat had long battled high blood pressure, a condition that made daily life difficult. Along with the hypertension, she also suffered from an ulcer. Her first response was to visit multiple hospitals in search of relief. “I visited four hospitals in the community,” she recalled. “But the doctors would just tell me to avoid salty foods and prescribe medication, which didn’t seem to help much.” Despite these efforts, her condition continued to worsen, and the burden of managing her health became overwhelming.
Hafsat eventually sought alternative treatment at other hospitals, hoping for a clearer diagnosis and solution. However, her visits were met with confusion. “They told me my condition wasn’t clear, and I was referred to other hospitals. It felt like I was running in circles. Nothing seemed to work.”
In the midst of these frustrating experiences, Hafsat learned about the REACH Clinic, a local healthcare facility that was part of the DIIAN project and provided free medication for patients with chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes. “I live close to the clinic, so I knew about it. When I found out they were offering free medication, I decided to give it a try,” Hafsat explained.
The change was immediate. Upon her first visit to the REACH Clinic, Hafsat was welcomed by a team of professionals who immediately began managing her hypertension with the right medication. “The difference was so clear. At other hospitals, I was often told they didn’t have the medication I needed or I would get prescriptions that didn’t seem to work. But at the REACH Clinic, they gave me the proper treatment,” Hafsat said, her voice filled with relief.
Over time, Hafsat’s health improved significantly. The swelling in her body, a common symptom of her hypertension, began to subside. “The swelling stopped, and I felt much better,” she recalled. “Before, I was taking medicine that wasn’t effective, but the medication I received here really worked.”
For Hafsat, the experience of receiving free, reliable care has not only alleviated her physical symptoms but also restored her sense of hope. “Now, when I run out of medication, I don’t worry. I know I can come back and get more,” she said, smiling.
The impact of the DIIAN project, and particularly the REACH Clinic’s provision of free medication, has been profound for Hafsat. “I want others to know that they don’t have to suffer the way I did. I used to feel hopeless, but now I am doing well. I encourage anyone who has high blood pressure or diabetes to get treatment, it makes all the difference,” she urged.
Looking forward, Hafsat’s outlook on life has been transformed. “I may not have any major ambitions right now, but I just want to stay healthy and continue receiving the care that has helped me so much. I am grateful for everything the REACH Clinic has done for me,” she concluded.
For Hafsat, the free medication provided through the DIIAN project has been life-changing, offering her a new sense of wellbeing and hope. Her story highlights the crucial role of accessible healthcare in improving the lives of vulnerable individuals and underscores the importance of initiatives that support those in need.