Tijesu Ojumu

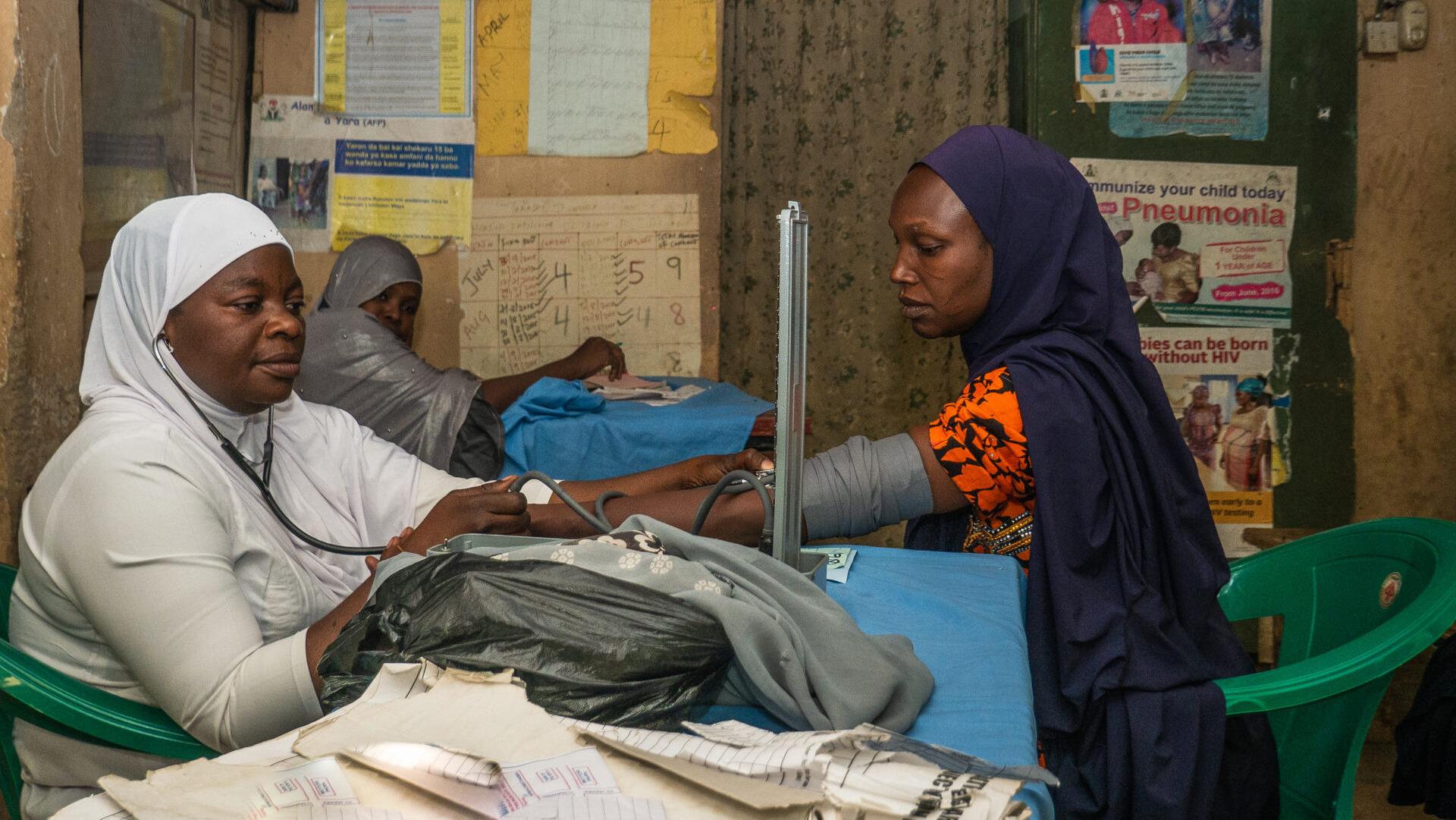
In boardrooms, conference halls, and digital health roundtables across Africa, the conversation is changing. It’s no longer just about deploying technology—it’s about designing systems that last, policies that enable, and innovations that scale. And eHealth Africa isn’t just in the room for these conversations. We’re helping shape them.
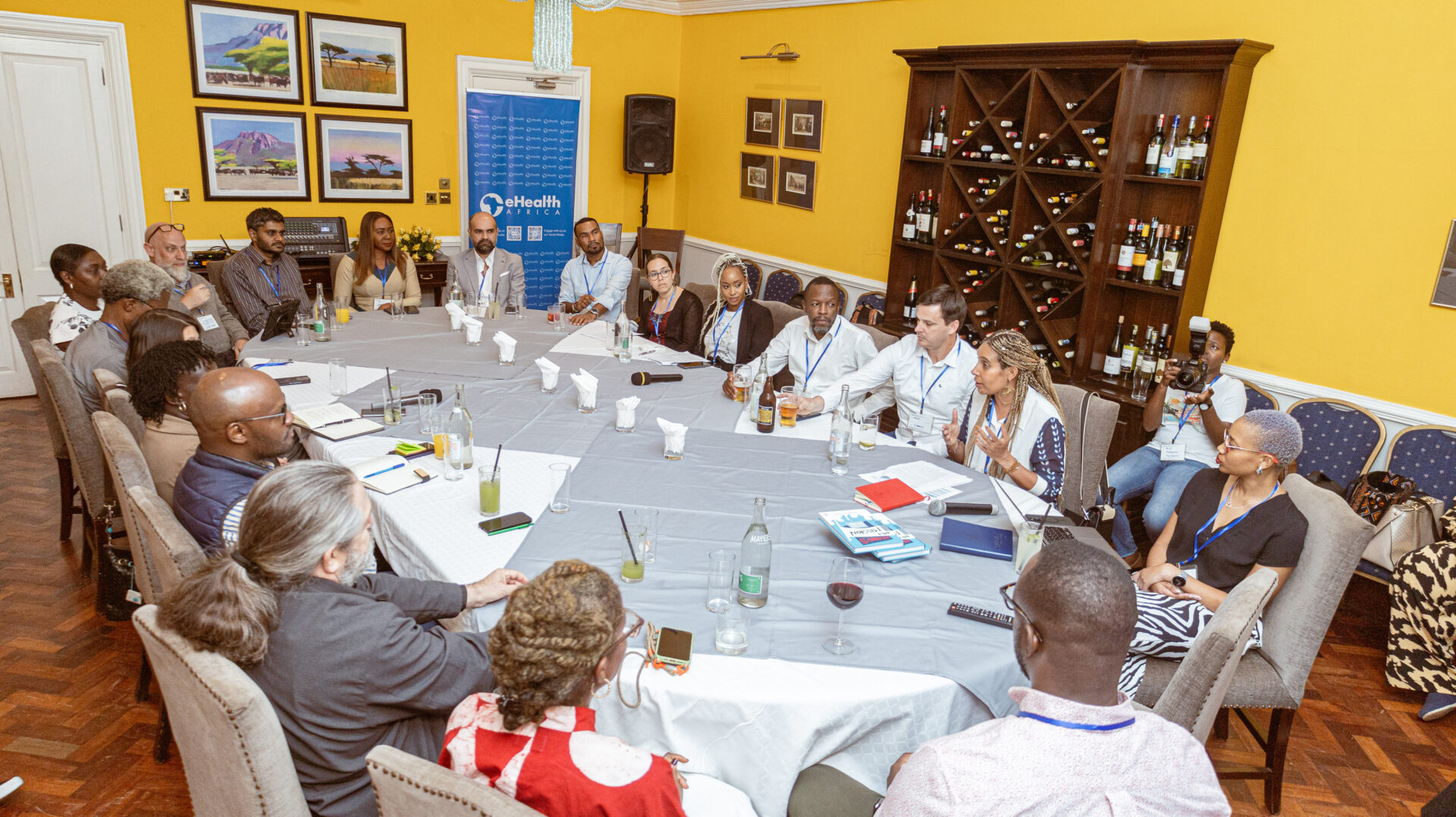
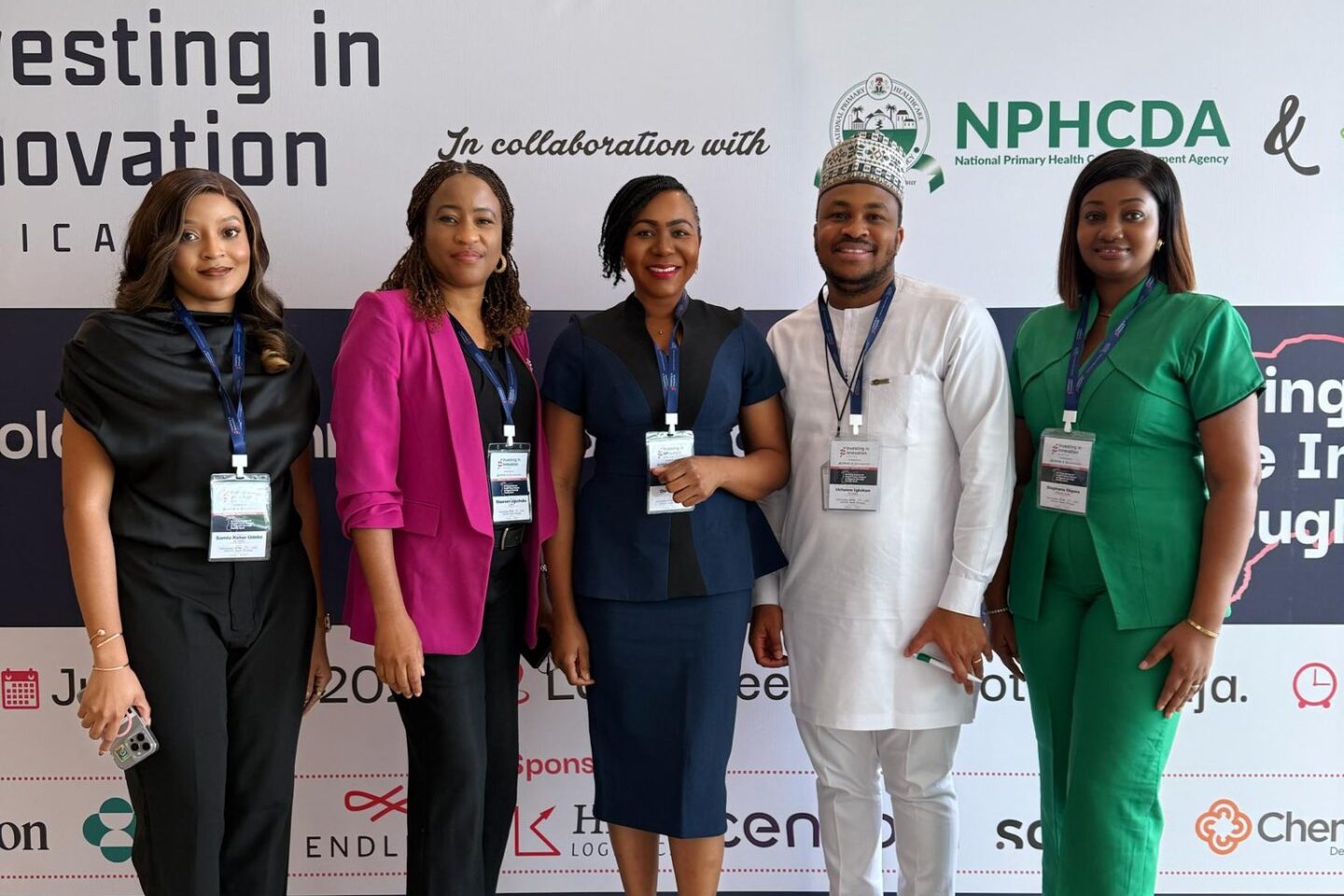
At a recent Stakeholder Alignment Workshop on Health-Tech Innovations for Advancing Universal Health Coverage, hosted by the leadership of the National Primary Healthcare Development Agency, Solina Centre for International Development and Research (SCIDaR) and the leaderships of CCHub, Salient Advisory, and the i3 team, eHealth Africa’s leadership was represented by the Director of Partnerships and Programs, Ota Akhigbe whose remarks emphasised that the future of health in Africa is about aligning innovation with national strategy, embedding it into real systems, and measuring what truly matters; equitable outcomes.
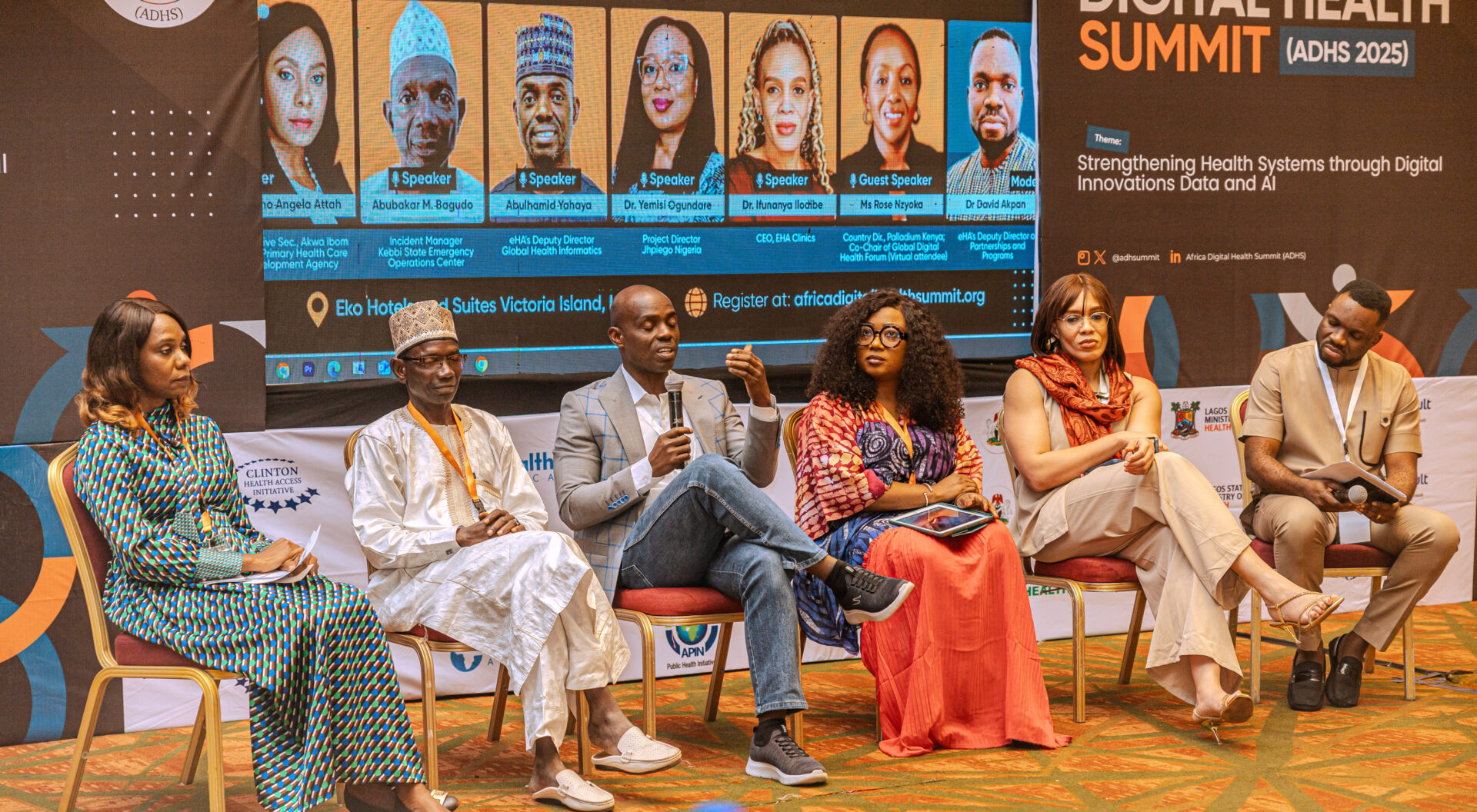
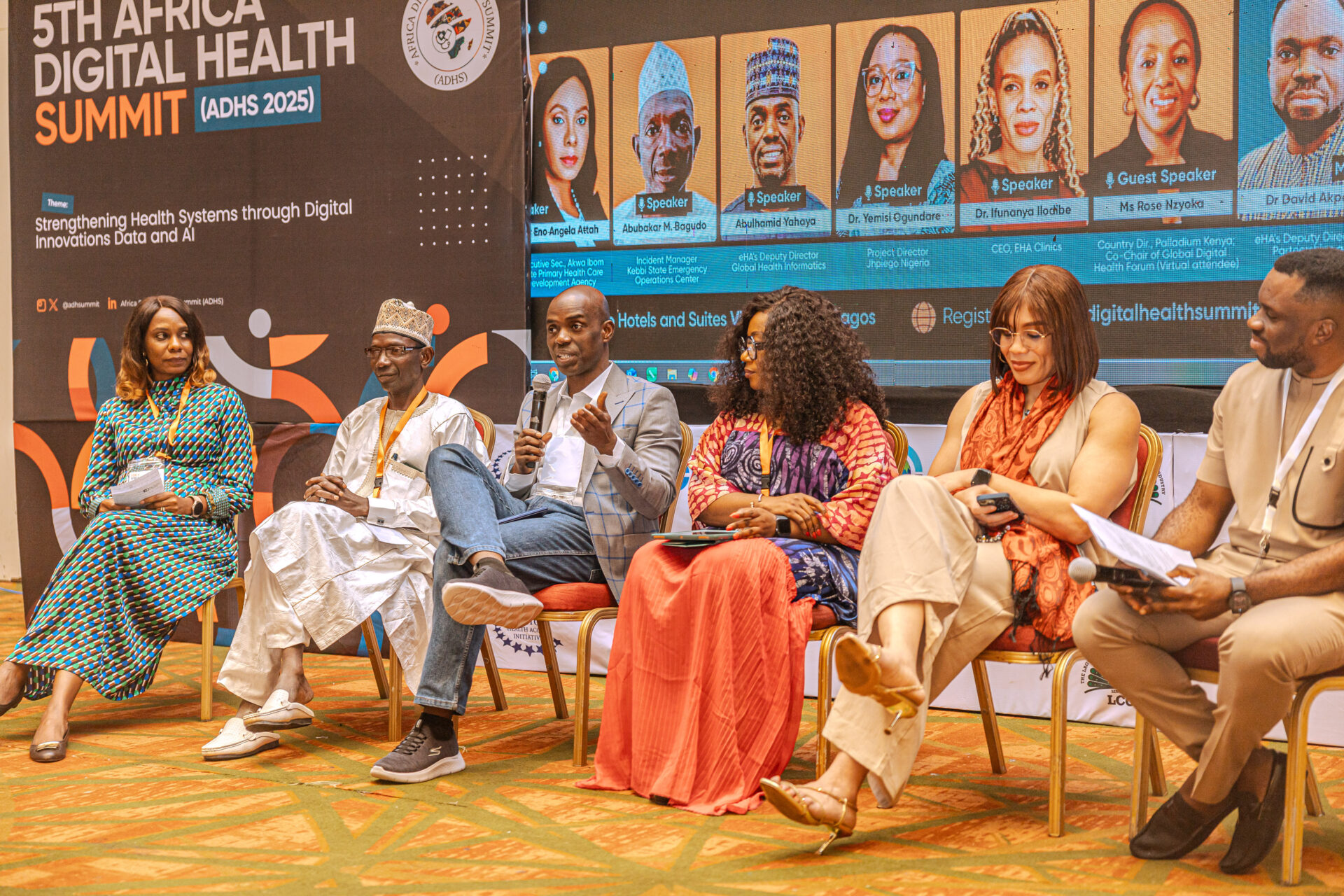
At the recently concluded Africa Digital Health Summit 2025, eHealth Africa Deputy Director, Programs and Partnerships- Dr. David Akpan co-chaired a session and what emerged was a refreshing reminder that innovation isn’t always about the newest, flashiest tools. As Dr. David put it, “Innovation can be as simple as improving an existing process. If it makes it easier, faster, more accessible—then it’s innovation that matters.”
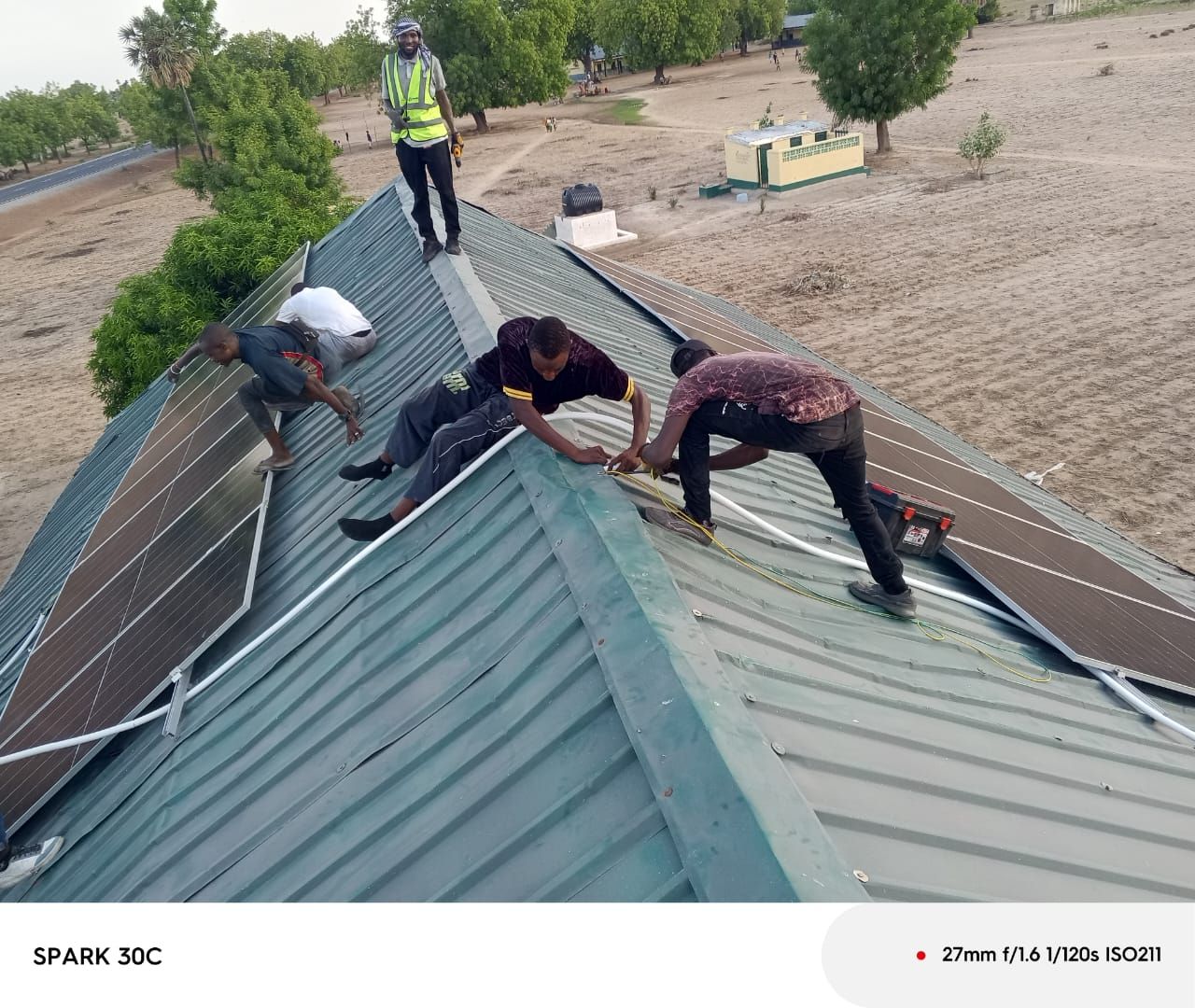
This focus on relevance and usability is central to eHealth Africa’s mission. Over the years, we’ve deployed digital health solutions across West and Central Africa, but what has remained consistent is our belief in building tools with, not just for, health systems.
From supporting national campaigns with GIS and real-time dashboards, to co-developing platforms like Planfeld for microplanning and outbreak response, our work bridges the gap between field realities and digital opportunities.
Our presence at policy workshops, innovation forums, and high-level summits isn’t accidental. It reflects a shift in how eHealth Africa is viewed across the continent: not just as a technical partner, but as a thought partner. We bring field-tested experience, deep partnerships with governments, and a practical lens that balances ambition with implementation.
Why does this matter? Because Africa’s digital health future won’t be driven by theory alone. It will require influence. Influence that is earned through delivery. Influence that helps shape funding priorities, regulatory frameworks, and capacity development.
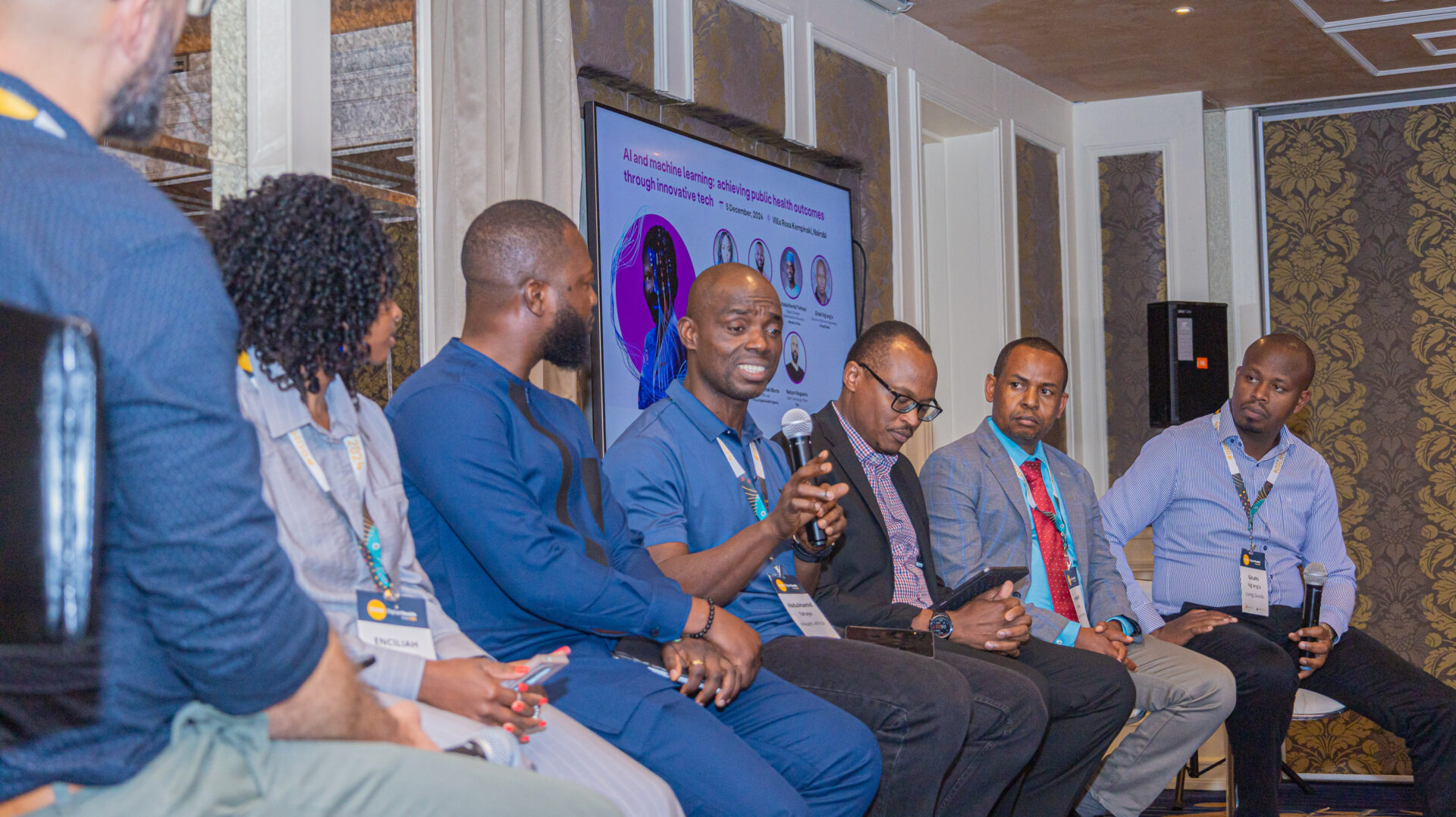
When we sit on panels, moderate discussions, or present research at summits like ADHS or ILF, we’re not there to just showcase tech. We’re there to advocate for approaches that work. To ask tough questions about inclusivity, equity, interoperability, and long-term system fit. To amplify the voices of field workers, innovators, and underrepresented communities.
And it’s working. More governments are requesting support not just to run programs, but to co-design policy blueprints. More funders are asking how to align their interventions with existing local infrastructure. More innovators are looking to us as conveners and collaborators.
The health-tech landscape in Africa is maturing. And eHealth Africa is proud to be part of the cohort helping define what comes next.
Because in the end, influence isn’t about the microphone—it’s about the message. And our message is clear: If we want systems that last, we must design them together.
To explore how eHealth Africa contributes to policy and partnership development in digital health, visit ehealthafrica.org or follow @eHealthAfrica.