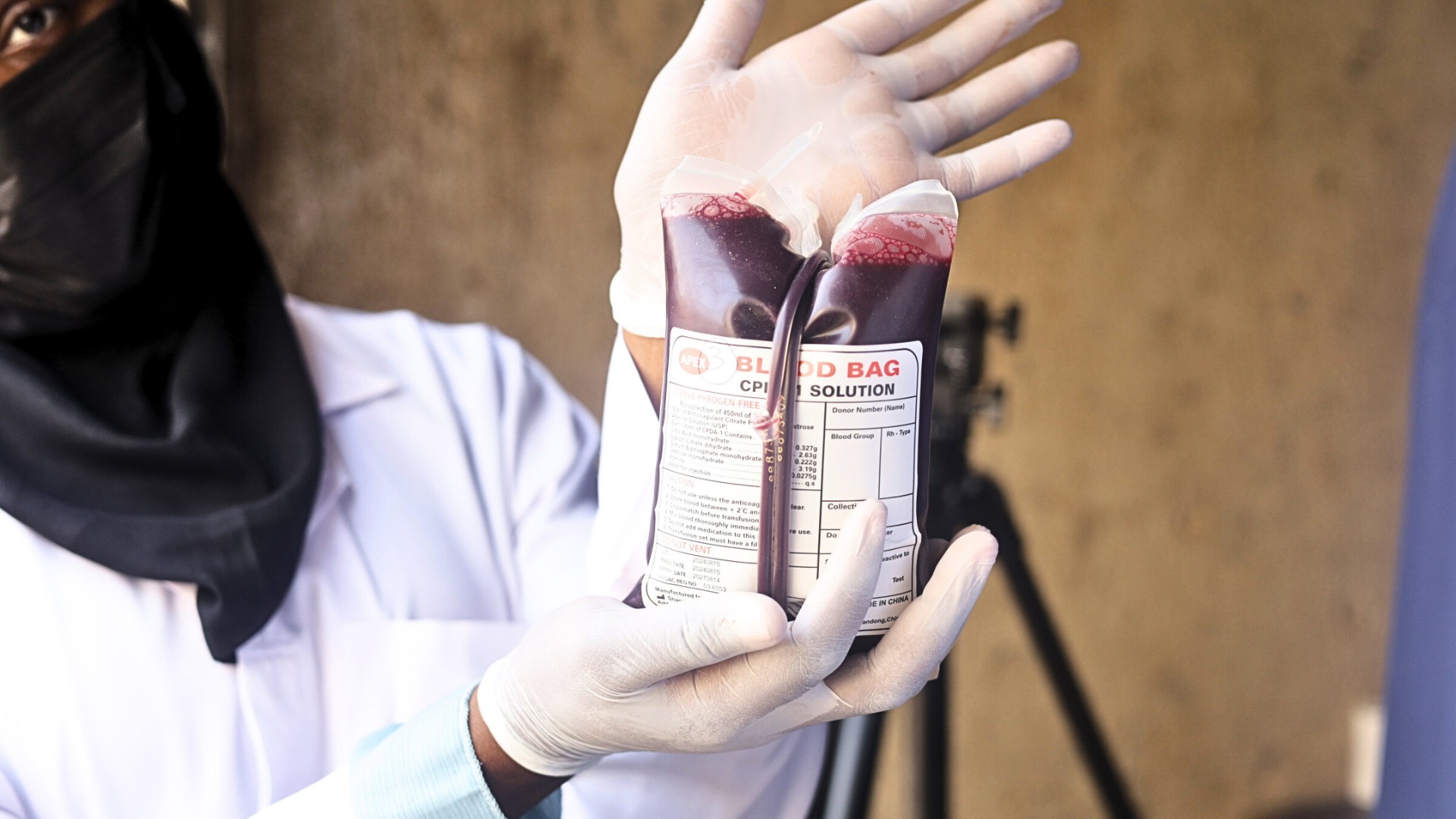
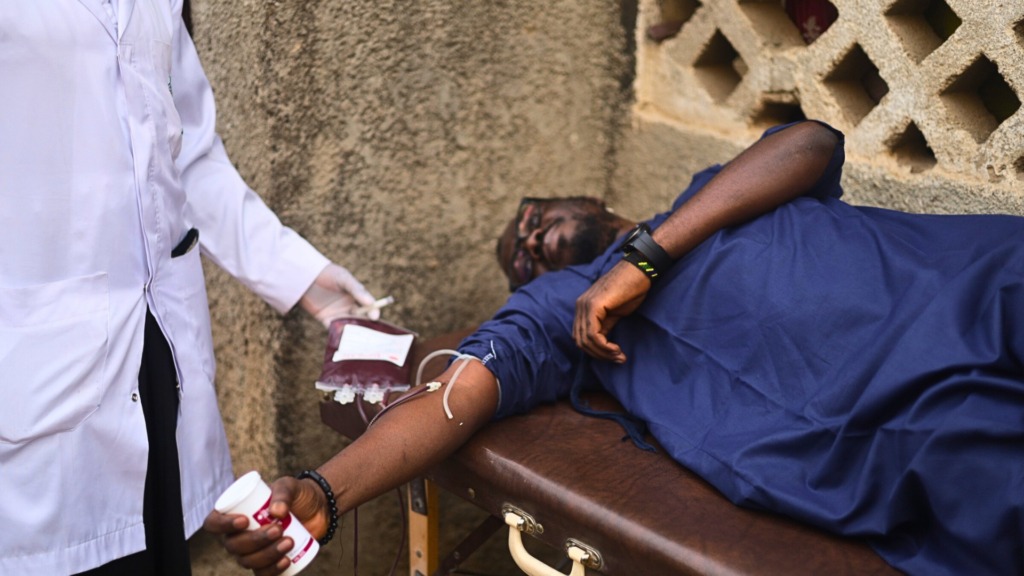
Tijesu Ojumu
In the latest episode of Insights Webinar (Ep. 32), eHealth Africa gathered health leaders, field experts, and technologists to tackle a pressing question:
“How can we strengthen the frontline health workforce to build resilient, effective health systems?”
This conversation went beyond theory—grounded in real-life stories from Nigeria and across Africa. It revealed that empowering frontline workers isn’t just a matter of investment—it’s the cornerstone of sustainable public health.
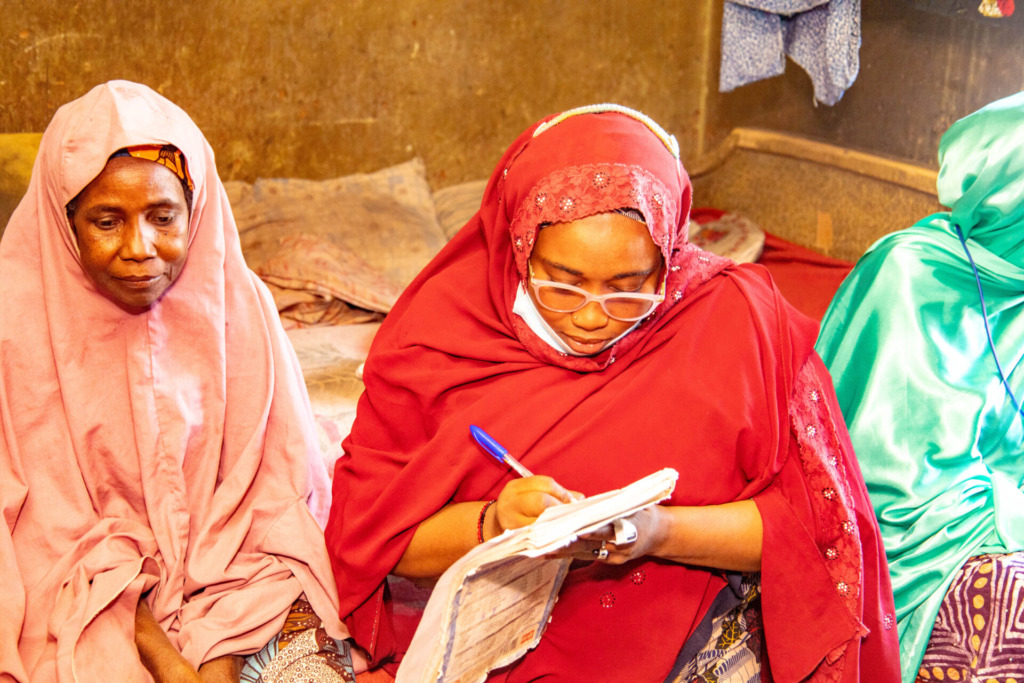
Across Nigeria and much of Africa, health systems are only as strong as the people who carry them. Community health workers. Surveillance officers. Data collectors. Midwives. These frontline actors form the invisible spine of the healthcare system. Yet too often, their voices, tools, and training are the last to be prioritized.
This was the urgent focus of a recent eHealth Africa-hosted webinar titled “How Do We Strengthen the Frontline Health Workforce to Build Resilient Systems?” Held as part of the Insights Webinar Series, this virtual conversation gathered public health leaders, digital health experts, and frontline practitioners to confront a truth that cannot be ignored: there is no strong health system without a strong frontline workforce.
Why Frontline Health Workers Matter More Than Ever
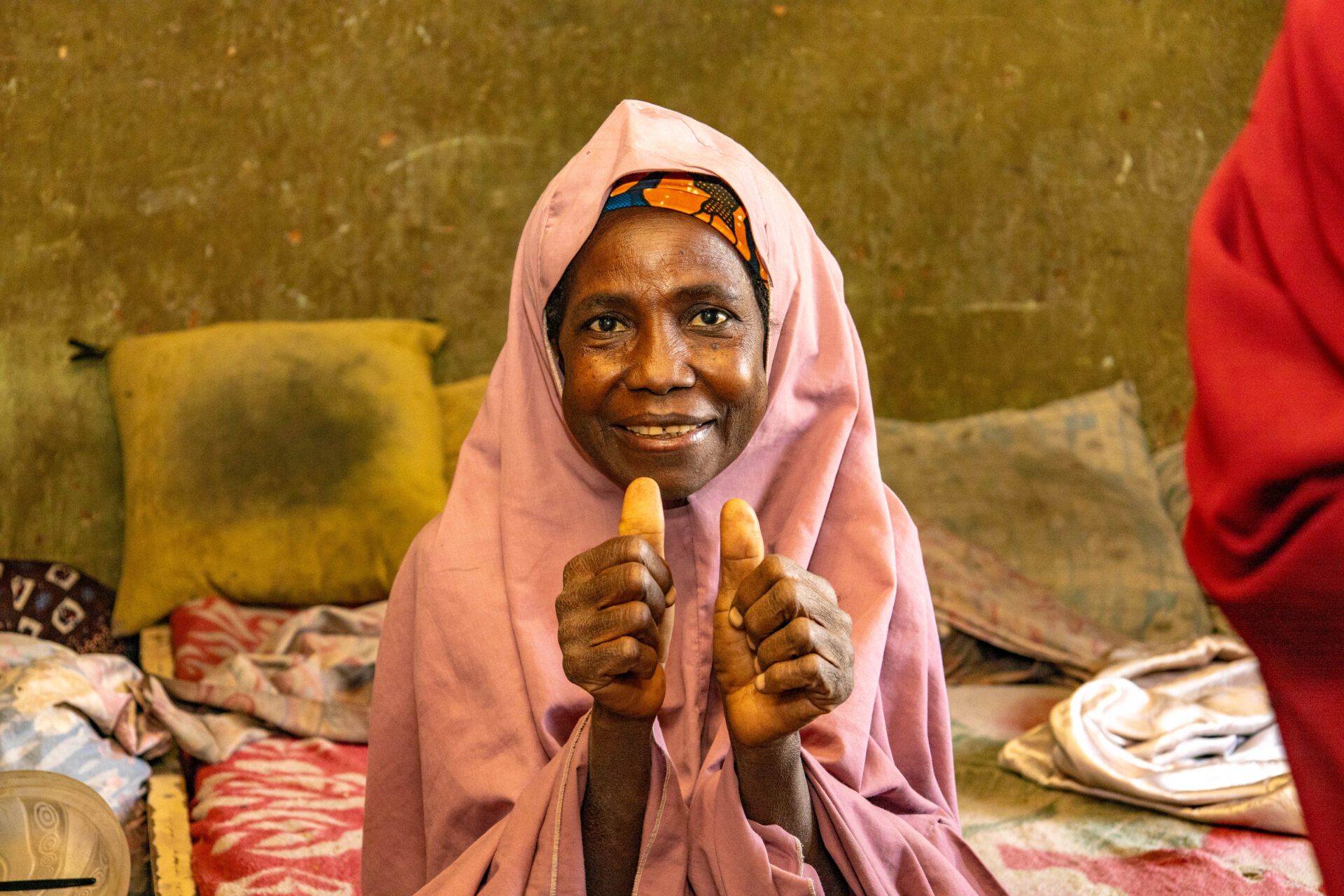
In an era of pandemics, climate-linked outbreaks, and rising health demands, the frontline workforce must be empowered—not stretched thin. The stories shared during the webinar were vivid. A health worker in Bauchi recounted how, using eHealth Africa’s microplanning tool, Planfeld, she helped identify a remote settlement that had been missed in previous immunization campaigns. Her digital training enabled her to map and reach families, ensuring over 200 children were vaccinated.
These stories, while inspiring, also reveal a gap: our systems cannot scale if the people on the ground are unsupported.
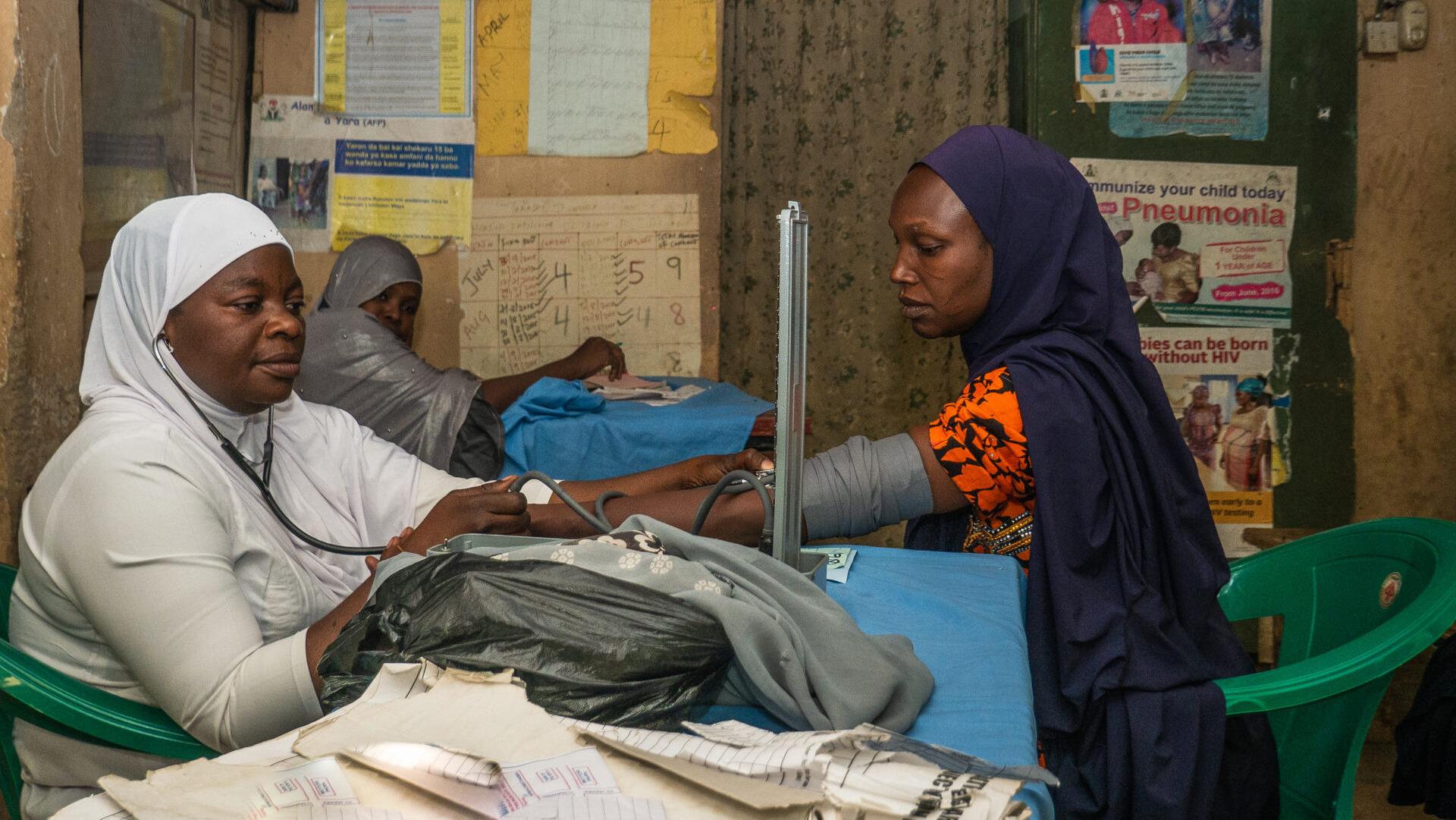
What Makes a Resilient Health Workforce?
According to the panelists, resilience is not about working harder—it’s about working smarter. And smarter systems require deliberate investment in three pillars:
1. Tools That Work Where the Roads Don’t
Digital tools are only effective when they fit the reality of field workers. The success of platforms like Planfeld in places like Kebbi and Lagos stems from their design: offline functionality, ease of use, and integration into daily health tasks. When CHWs can carry tools that work regardless of network coverage, data improves, and so does decision-making.
2. Training That Doesn’t Stop After Day One
Introducing a new app or system is just the beginning. True transformation happens when health workers receive ongoing mentorship and support. Webinar participants cited cases where follow-up sessions led to 30% improvements in data quality. Iterative learning, not one-off workshops, is the foundation of workforce development.
3. Systems That Listen Back
Collecting data is important. Acting on it is essential. The most resilient systems create feedback loops where CHWs, supervisors, and planners can respond to what the data reveals. One technical advisor shared that a nurse who flags a vaccine stockout should expect a response the next day—not weeks later. Otherwise, the system loses credibility.
Elevating Local Expertise
An important theme echoed throughout the session: those closest to the problem are often closest to the solution. When health workers participate in the design and rollout of digital tools, uptake and sustainability improve. Several speakers emphasized the value of “co-creation,” where CHWs and local stakeholders help shape the very systems they are expected to use.

Lessons for Donors and Partners
For partners, funders, and development agencies, the path forward is clear:
- Integrate technology and training. Don’t fund digital platforms without allocating resources for hands-on, repeated training.
- Support pilot-to-scale models. Programs that start small and evolve with user feedback are more likely to succeed.
- Invest in supervision and follow-through. Data must lead to action. Tools are only as strong as the systems they plug into.
- Make frontline workers visible in policy. Include their needs, voices, and priorities in health systems planning.
Building the Future, One Worker at a Time
eHealth Africa continues to embed these principles across its programming. From early disease detection to microplanning and cold chain logistics, frontline workers are central to every success story.
The vision is clear: a health system where digital tools serve people, not the other way around. Where midwives, CHWs, and health informants have the tools they need, the training they deserve, and the power to shape decisions.
Because ultimately, health systems don’t fail because technology is lacking. They fail when the people who carry them are left behind.
And if we truly want resilient systems, we must begin at the base—by backing the backbone.
Want to explore more?
Watch the full webinar here: https://youtu.be/gmaNtXPsG2M
Visit ehealthafrica.org to learn how we’re supporting health workers through technology, training, and partnership.