May 8, 2025
BISKIT: Bridging the Gap in Blood Information Management System
By – Fatima Abdulaziz Ayomitide
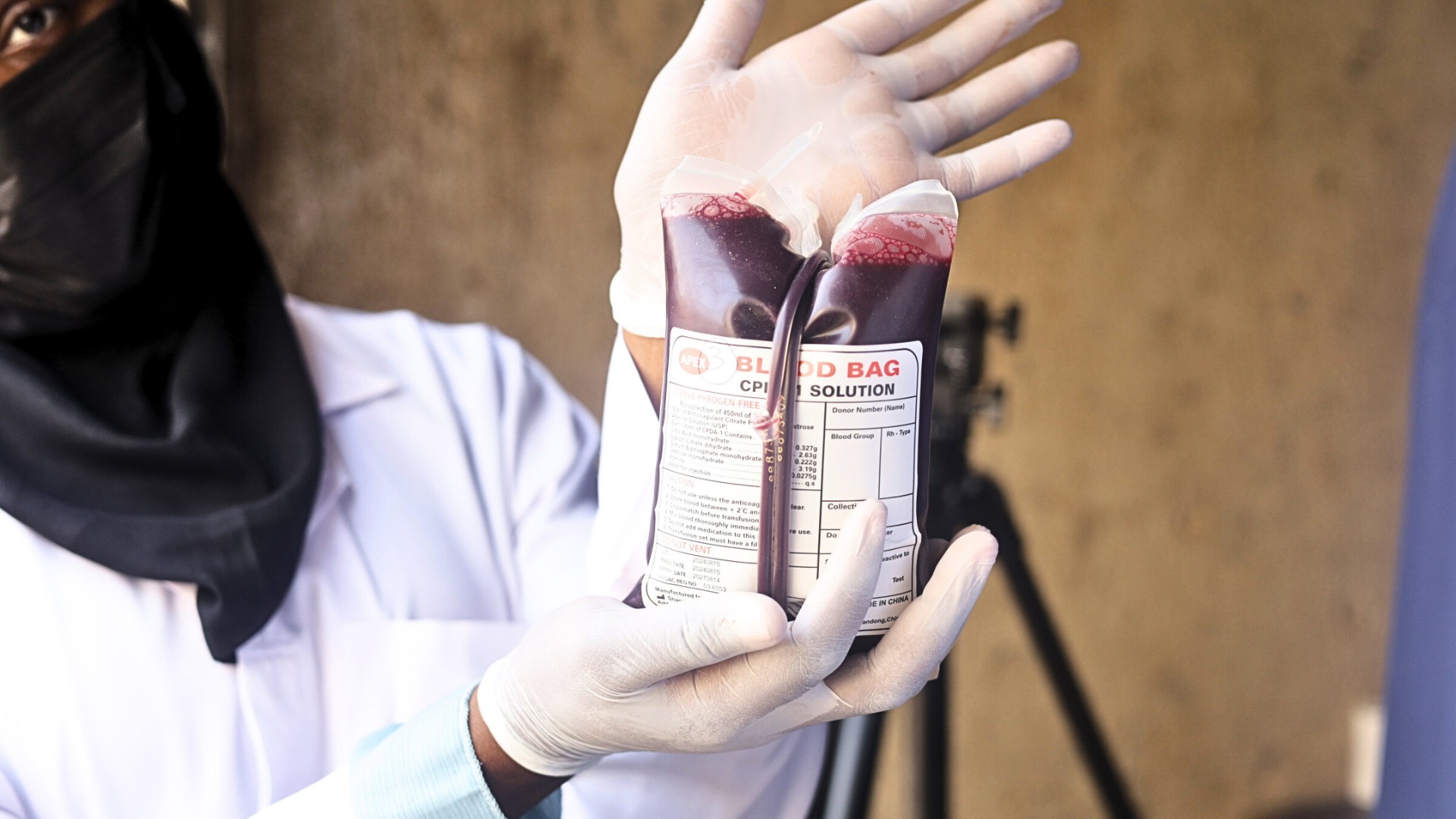
The persistent and critical blood shortage in Nigerian hospitals, as revealed by the National Blood Service Agency (NBSA) in December 2024, shows that Nigeria can only meet less than 30% of its blood transfusion needs. This severe deficit creates a life-threatening situation for patients and strains hospital resources, particularly during emergencies. The World Health Organization has also estimated that 1.5 million units of blood are needed annually to meet healthcare demands, yet only about 500,000 units are collected each year. This shortfall of nearly 67% has serious implications for patient care. Emergency cases often depend on last-minute donations, and in some instances, the available stock is either insufficient or compromised due to poor storage practices.
Underlying this crisis is a deeper issue of uncertainty. Donors, even those who regularly volunteer, are often left questioning where their blood goes, who it helps, and whether it makes the intended impact. This lack of transparency discourages participation, especially among first-time donors.
Evidence suggests that potential blood donors in African countries are more inclined to donate when they have a clearer understanding of how their contributions are utilized. Recognizing this desire for transparency and impact, a team of researchers and technologists began exploring how digital tools could build trust and improve the efficiency of the blood donation system.
Among them is Mohammed-Faosy Adeniran, the Project Manager for BISKIT, short for The Blood Information System for Crisis Intervention and Management (BISKIT), a mobile-based platform developed by eHealth Africa to address some of these critical gaps. “We realized the problem wasn’t a lack of willingness to donate but a disconnect between that willingness and actual blood requests. There were willing donors on one end, and urgent needs on the other, but no real-time system to link them.”
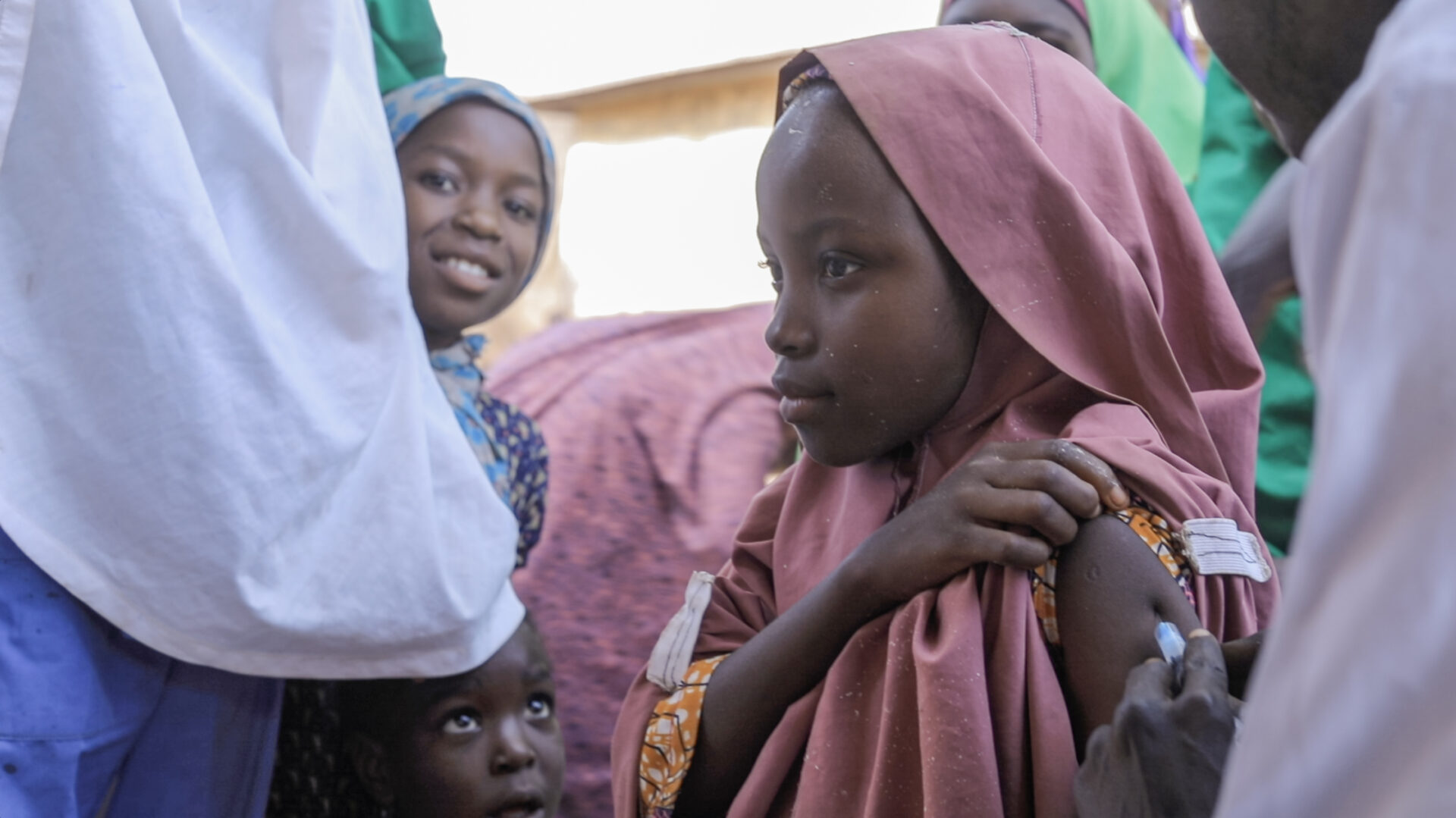
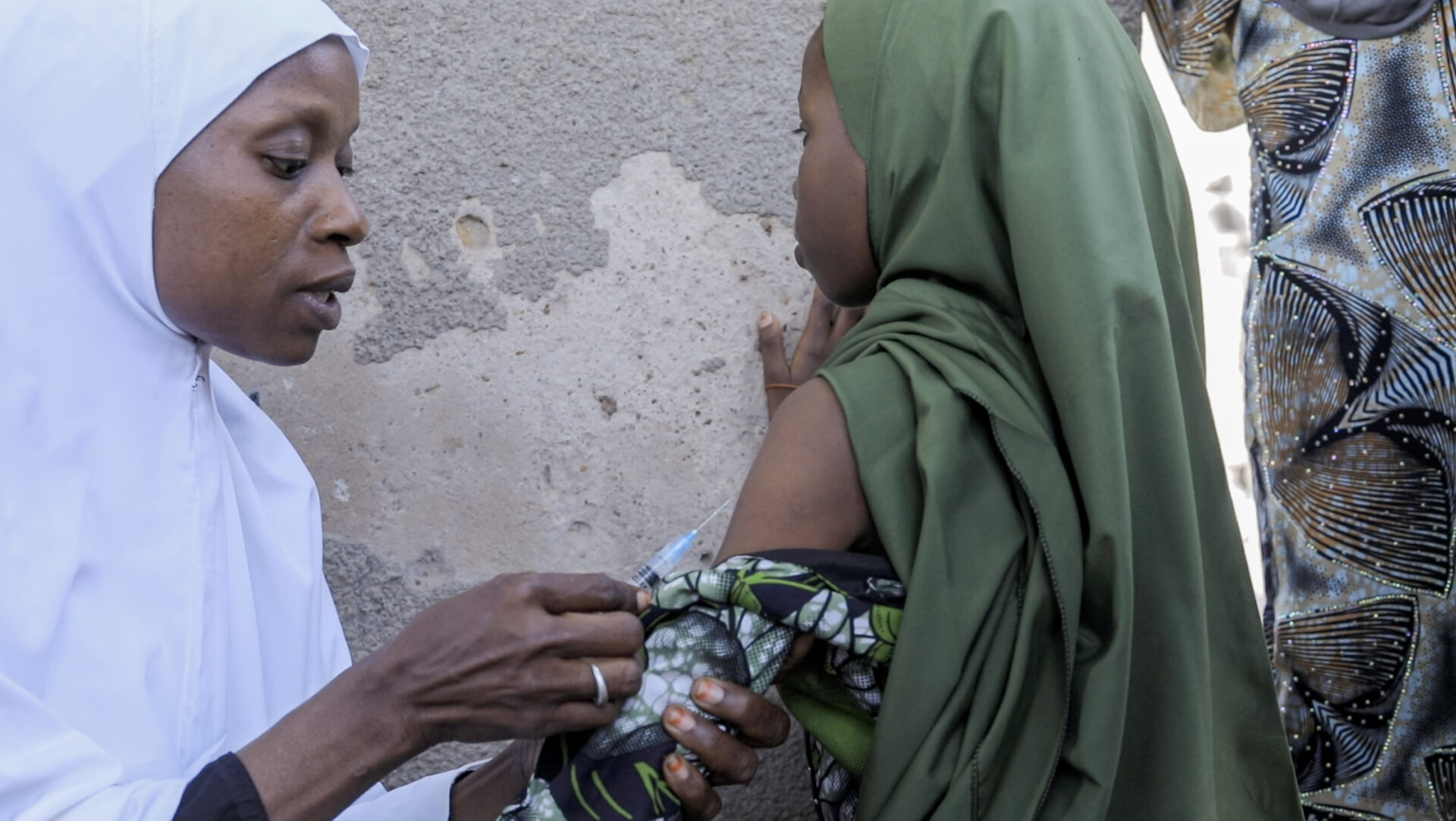
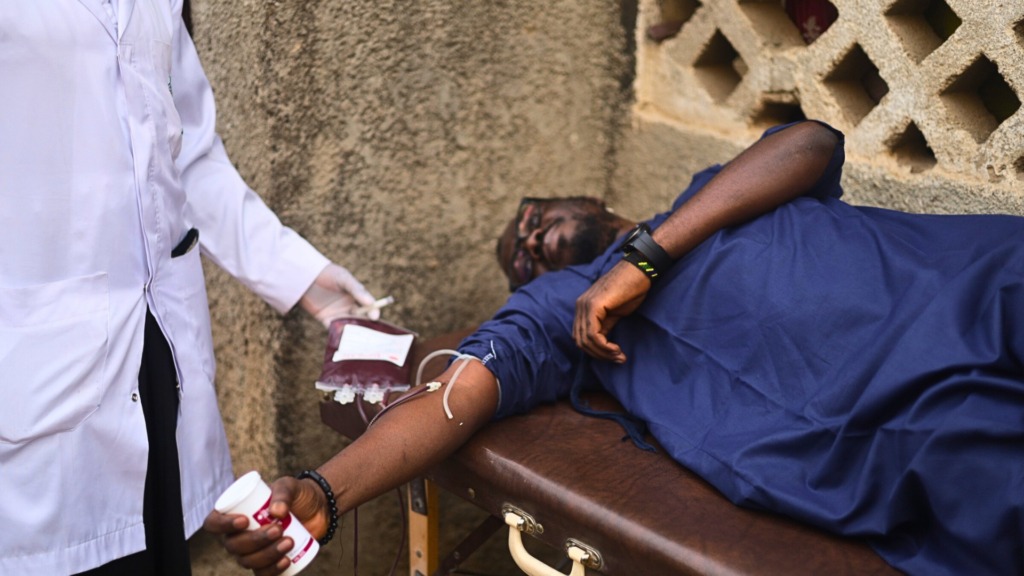
According to him, eHealth Africa is currently piloting the use of BISKIT at the Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital in Kano state. This is in a bid to standardize the digitization of blood information and management systems. During this implementation, the application allows users, donors, health workers, hospitals, and blood banks to manage and track blood donations from start to finish. Built with offline and mobile capabilities, BISKIT can function even in areas with limited internet access, ensuring wider reach and usability.
Halima Kabir Abdulkadir, a Research Assistant whose role involves performing cross-matching for patients, emphasized the complexity of managing donor and recipient data. “It contains a lot of information from the donors to the recipients. Having everything tracked in one system helps reduce errors and makes the process more efficient.”
For instance, when a health worker submits a request, nearby donors registered on the app are notified immediately. Through this direct and efficient channel, response times are reduced significantly.
Beyond logistics, the app also focuses on building trust. For donors, BISKIT offers a more transparent experience. They receive updates about their donations, pre-book appointments, and are guided through the donation process especially helpful for newcomers. “People just want to know their effort counts,” said Faosy. “The feedback we’ve received shows that donors are more encouraged to return when they can see the impact of their contribution.”
He added that the BISKIT application seeks to tackle structural issues like blood wastage. By integrating Geographic Information Systems and barcode tracking, BISKIT makes it easier to monitor the location and condition of blood bags, helping prevent mishandling or loss.
While still in its early stages of rollout, the platform has already shown promise. In pilot locations like Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano state, health workers report faster donor mobilization and fewer delays in emergency response.
Ultimately, BISKIT presents a compelling case for how technology can bridge gaps in public health systems, especially in contexts where trust, efficiency, and transparency are critical. Whether this model can scale across the country or even regionally remains to be seen. But for now, the app offers a practical solution to an urgent problem and a hopeful shift toward a more connected and accountable blood donation ecosystem.
Fatimah Azeez-Ayodele Ayomitide is a communications intern at eHealth Africa







